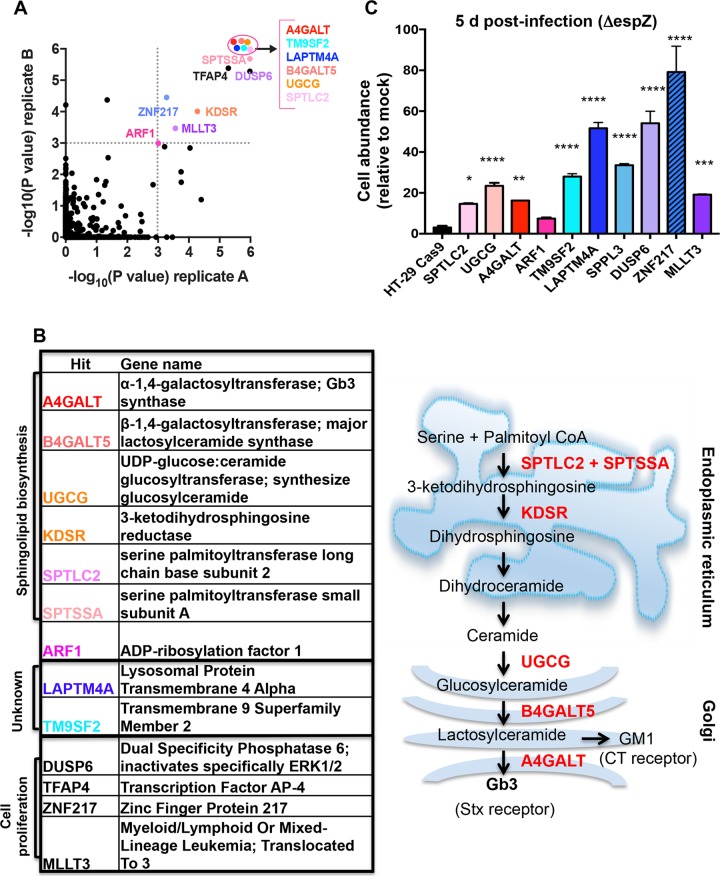
FIG 2 .
Mutations that disrupt sphingolipid biosynthesis and poorly characterized genes are enriched in the HT-29 CRISPR/Cas9 library following repeated infection with espZ EHEC. (A) Scatterplot of the statistical significance in each library (A and B) associated with the genes ranked in the top 5% by the STARS algorithm. Genes with a P value of ≤0.001 in both libraries (upper right quadrant) are named; genes within the ellipse all have P values of <2.0e−06. (B) Products of genes shown in panel A with P ≤ 0.001 in both libraries and schematic representation depicting the subcellular localization of enzymes (black) that contribute to sphingolipid biosynthesis. A subset of substrates/products is depicted in red. (C) Abundance of HT29 control and mutant cells infected with ΔespZ EHEC relative to the abundance of mock-infected cells at day 5 postinfection. Graphs display the mean and SD from 3 independent experiments compared to HT-29 Cas9 (leftmost bar). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.