Figure 6. Lymphocyte migration stimulates dissociation of ZO-1 from endothelial cell junctions.
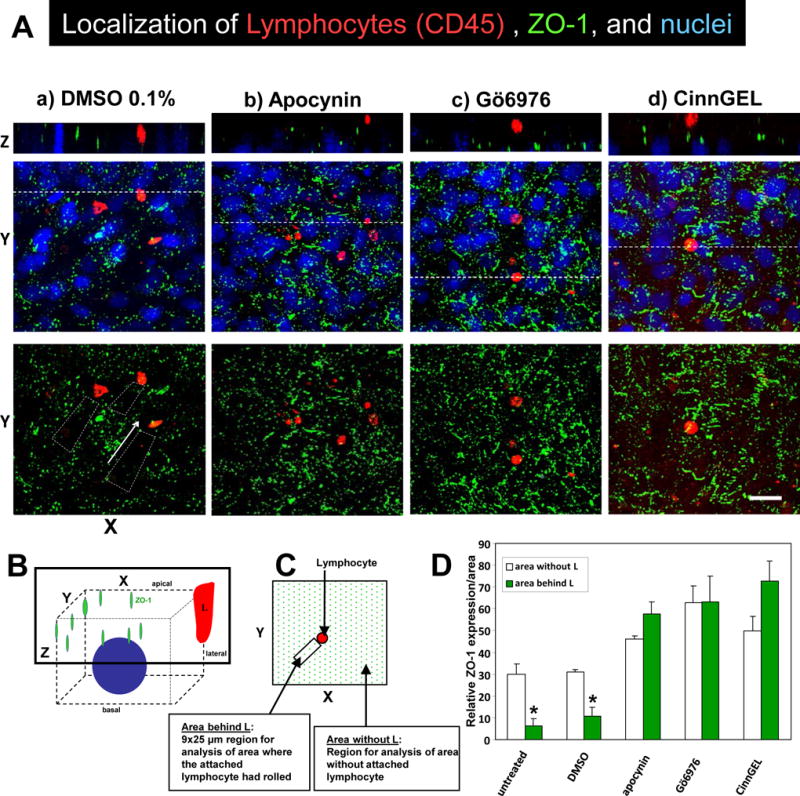
A) Confluent monolayers of mHEV cells were non-treated or pretreated for 30 minutes with 0.1% DMSO vehicle control, 4 mM apocynin, 2.3 nM Gö6976 or 10μM CinnGEL-2ME. The monolayers were washed 5 times, placed in a parallel plate flow chamber and then lymphocytes were added for 15 minutes under 2 dynes/cm2 laminar flow. The monolayers were fixed and immunolabeled for ZO-1 (green) and CD45 (red). The nuclei (blue) are labeled with 1 μg/ml DAPI. The fluorescence was examined by confocal microscopy and representative micrographs of 3 experiments are shown. Shown are XY on-face of 3D images or a Z-stack of the images at the location of the dotted line in the panel below it. Arrows indicate the direction of laminar flow. Bar, 20 μm. B) Diagram of 3D confocal analysis. C) Diagram of 9×25 μm XY regions of the Z stack behind the lymphocyte that was analyzed for intensity of labeling of ZO-1 in the Z stack. D) Relative intensity of ZO-1 labeling/area in the 9×25 μm XY regions of a Z stack as described in panel C. Data are from 3 experiments and presented as mean ±SEM. *, p<0.05.
