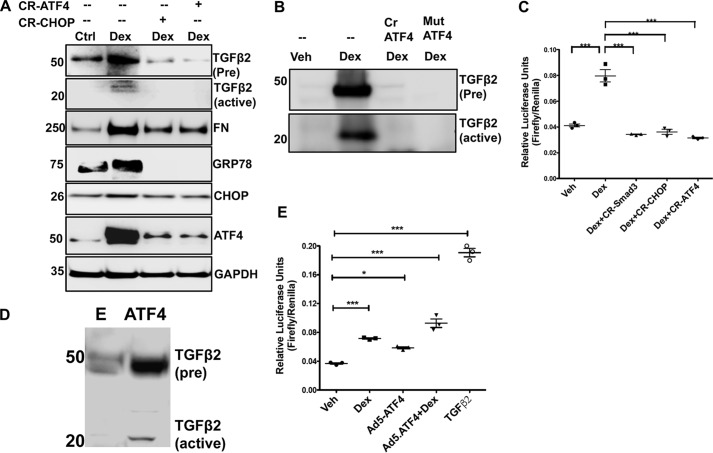
Figure 9.
Chronic ER stress–induced ATF4 and CHOP are involved in Dex-induced TGFβ2. A, GTM3 cells transiently transfected with CRISPR-Cas9-CHOP or CRISPR-Cas9-ATF4 and treated with Veh or Dex for 48 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for expression levels of fibronectin (FN), TGFβ2, and ER stress markers by Western blotting. Knockdown of ATF4 or CHOP inhibits TGFβ2 signaling and prevents abnormal Dex-induced ECM accumulation and ER stress in TM cells. n = 3 replicates. B, GTM3 cells were transfected with CRISPR-Cas9-ATF4 (Cr ATF4) or a dominant-negative inhibitor of ATF4 (Mut ATF4) and treated with Dex for 48 h. The conditioned medium was examined for TGFβ2 by Western blot analysis. n = 3 replicates. C, GTM3 cells, transfected with SMAD-luciferase and CRISPR-Cas9 targeting SMAD3 or CHOP or ATF4 constructs, were treated with Veh or Dex for 24 h. Knockdown of ATF4 or CHOP in Dex-treated TM cells prevented SMAD activation in a SMAD-luciferase assay (n = 3, one-way ANOVA). ***, p < 0.001). D, GTM3 cells were transduced with adenovirus 5–expressing ATF4 for 48 h. The conditioned medium was examined for TGFβ2 by Western blot analysis (n = 3 replicates). E = control adenovirus. E, GTM3 cells were transfected with SMAD-luciferase constructs and treated with Veh, Dex, or adenovirus 5–expressing ATF4 (Ad5-ATF4). Treatment with recombinant TGFβ2 was utilized as a positive control for activation of SMAD signaling. Both Dex and overexpression of ATF4 alone were able to increase SMAD-luciferase activity significantly. A combination of Dex with ATF4 overexpression further increased SMAD-luciferase activity compared with ATF4 alone. n = 3, one-way ANOVA; *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001.