Figure 1.
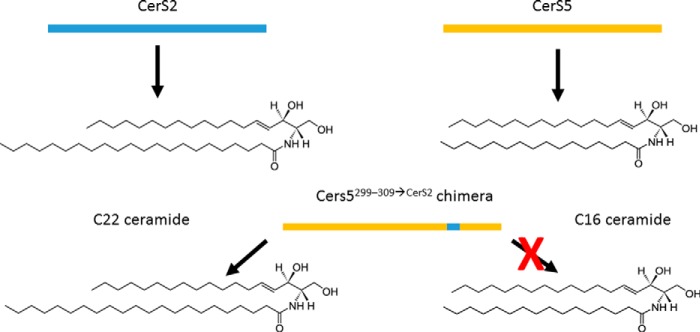
An 11-residue segment in ceramide synthases determines substrate (and product) specificity. When 11 amino acids in a loop located between the last two putative transmembrane domains from CerS2 replace the corresponding residues in CerS5, the chimeric protein CerS5299–309→CerS2 produces C22-ceramide (a typical CerS2 product) instead of the C16-ceramide that CerS5 normally produces.