Figure 1.
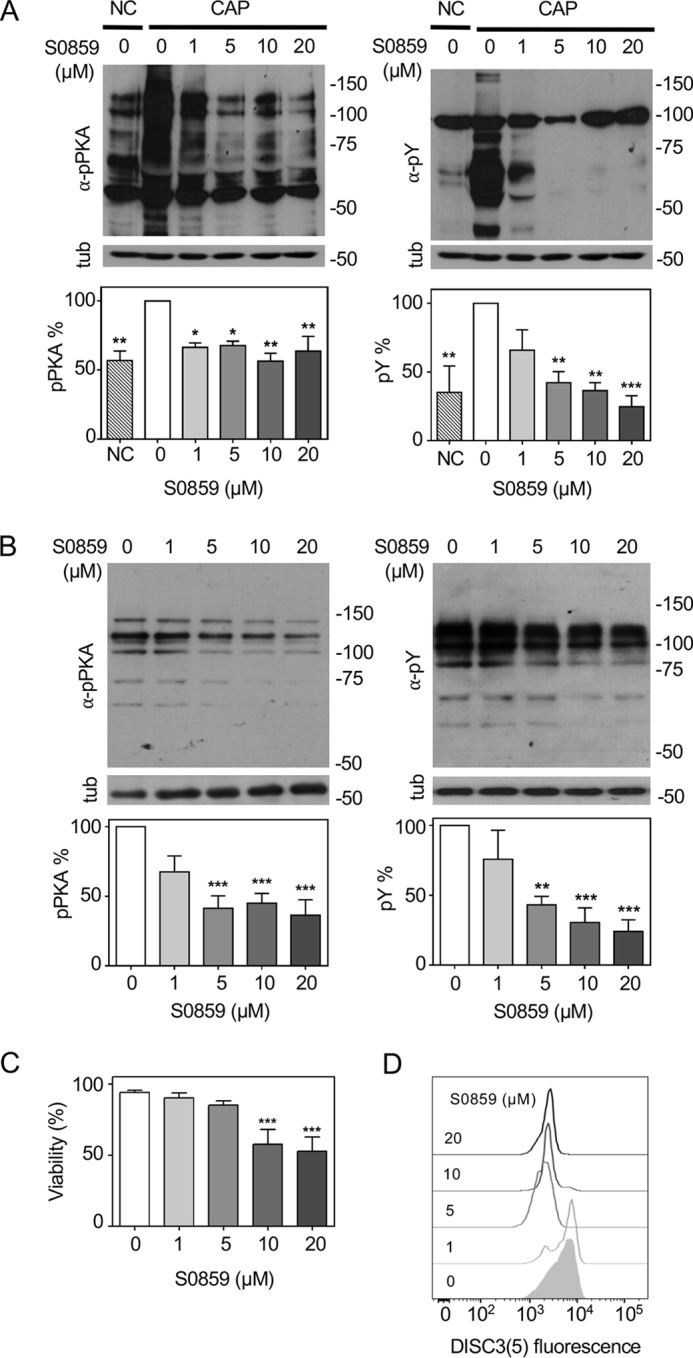
NBC is necessary for activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway and Em regulation during human sperm capacitation. A, mouse sperm were incubated in CAP for 90 min with different concentrations of the NBC inhibitor S0859. Sperm were also incubated under noncapacitating condition (NC); in the absence of HCO3− and BSA. Aliquots from each condition were processed for Western blotting with anti-pPKA (left panel) or anti-pTyr (right panel) antibodies and then membranes were reblotted with an anti-β-tubulin antibody for loading control (lower panel). Blots were quantified as described under “Experimental procedures” (bottom panel). Values represent the mean ± S.E. of at least 3 experiments. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. B, human sperm were incubated in capacitating medium with different concentrations of the NBC inhibitor S0859. Aliquots from each condition were processed for Western blotting with anti-pPKA (left panel) or anti-pTyr (right panel) antibodies and then membranes were reblotted with an anti-β-tubulin antibody for loading control (lower panel). Blots were quantified and values represent the mean ± S.E. of at least 3 experiments (bottom panel). ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. C, human sperm were incubated with different concentrations of the NBC inhibitor S0859 and the percentage of live cells was assessed by Eosin-Y staining. ***, p < 0.001 (n = 4). D, histograms of percentage of the maximum (% max) versus DISC3(5) fluorescence of BCECF positive cells. Human sperm were incubated in medium that supports capacitation with different concentrations of the NBC inhibitor S0859. Subsequently, aliquots from each condition were processed by flow cytometry to evaluate Em with DISC3(5) and with BCECF-AM to estimate viability.
