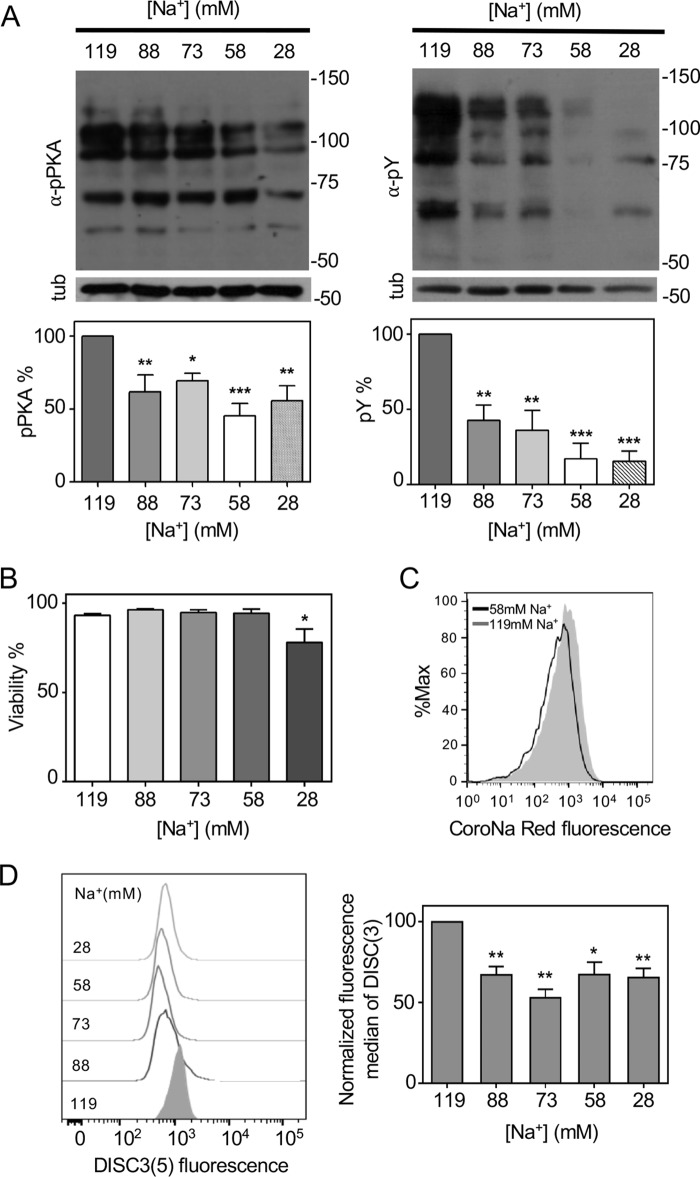
Figure 4.
[Na+]e is required for the capacitation-associated increased activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway and Em regulation during capacitation. A, sperm were incubated in capacitating medium with different Na+ concentrations. Aliquots from each condition were processed for Western blotting with anti-pPKA (left panel) or anti-pTyr (right panel) antibodies and then the membranes were reblotted with an anti-β-tubulin antibody for loading control (lower panel). Blots were quantified as described under “Experiment procedures” (bottom panel). Values represent the mean ± S.E. of at least 3 experiments. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. B, human sperm were incubated with different Na+ concentrations and the percentage of live cells was assessed using Eosin-Y. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3). C, histograms of percentage of the maximum (% max) versus CoroNa Red fluorescence of BCECF-stained sperm are shown. Human sperm were incubated for 5 h in medium that supports capacitation containing 58 mm Na+. Subsequently, aliquots from each condition were processed by flow cytometry to evaluate [Na+]i with CoroNa Red and BCECF to estimate viability. These experiments were repeated at least 3 times with similar results. D, histograms of percentage of the maximum (% max) versus DISC3(5) fluorescence of BCECF stained sperm are shown (left). Human sperm were incubated in medium that supports capacitation with different Na+ concentrations. Subsequently, aliquots from each condition were processed by flow cytometry to evaluate Em with DISC3(5) and with BCECF-AM to estimate viability. Fluorescence median of DISC3(5) was normalized with respect to 119 mm Na+ (right). Values represent the mean ± S.E. of 4 experiments. **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05 versus the sample with 119 mm Na+.