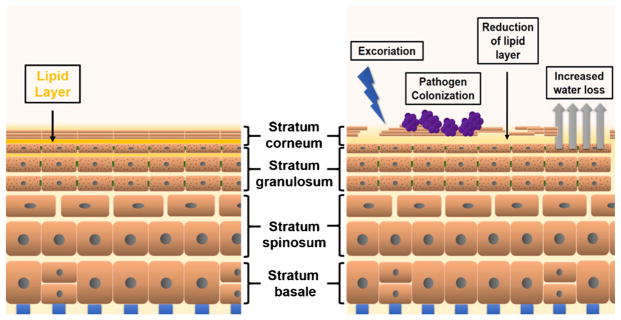
Fig. 1.
Barrier function in healthy and AD skin. Keratinocytes proliferate in the stratum basale and migrate to the stratum granulosum where lipids are secreted into the stratum corneum. The stratum corneum houses keratinocytes that have lost organelles, flatten, and eventually slough off. In AD, increased water loss is a result of a loss of the lipid layer surrounding corneocytes in the inner stratum corneum that acts as a barrier to water-soluble substances. With excoriation, pathogens such as S. aureus are able to colonize the skin more readily