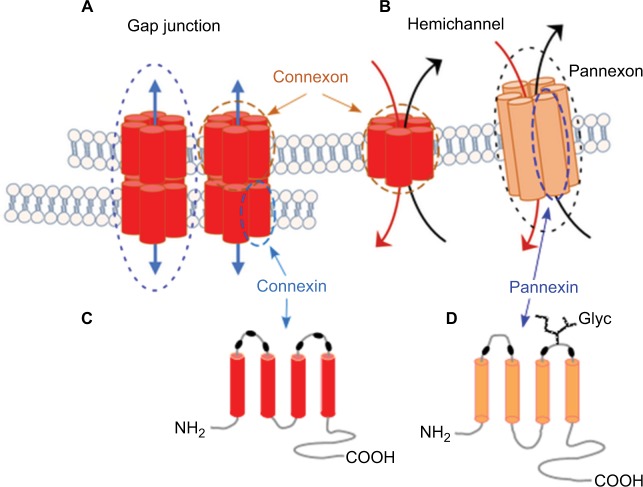
Figure 1.
Connexins and pannexins.
Notes: (A, B) Connexin and pannexin share a similar structure, despite the absence of sequence homology. Connexin and pannexin form functional connexon and pannexon hemichannels, respectively. (C, D) Connexins and pannexins are transmembrane proteins with four transmembrane domains, two extracellular loops, one cytoplasmic loop, and cytoplasmic N- and C-terminal domains. Connexin channels can assemble into a gap junction (A) that mediates intercellular communication, while pannexin’s extracellular loop has a high level of glycosylation in mammalian cells (D), which prevent the formation of gap junctions.
Abbreviation: Glyc, glycosylation.