Figure 2.
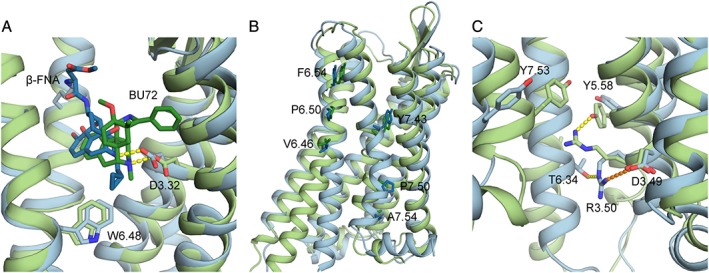
(A) Close‐up of the binding pockets of inactive and activated μ receptor crystal structures. Focus is on the salt bridges (yellow, dotted lines) formed by the amino group of β‐FNA (dark blue) and BU72 (dark green) and the side chain of D3.32 of the inactive (light blue) and activated (light green) crystal structures, respectively, as well as the hydrophobic interaction between W6.48 and β‐FNA; (B) residues of TM6 and TM7 used to calculate helix bending in (Cheng et al., 2016b); (C) residues involved in the ionic lock in inactive and activated μ receptor crystal structures. Shown as dotted lines are the salt bridge (orange) between D3.49 and R3.50 and the hydrogen bond (yellow) between T6.34 with R3.50 in the inactive μ receptor crystal structure, as well as the hydrogen bond (yellow) formed between Y5.58 and R3.50 in the activated crystal structure of the μ receptor.
