Figure 1.
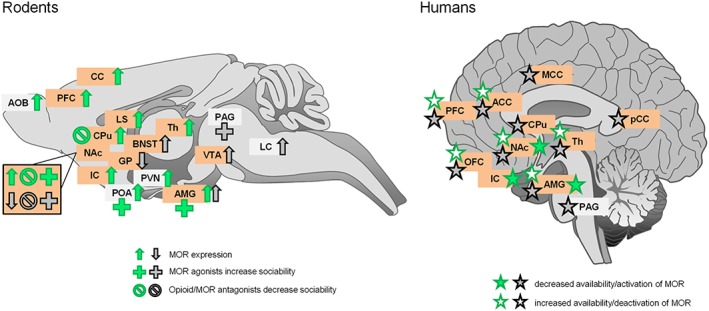
Effects of regional pharmacological manipulation of μ receptors (MOR) on social behaviour and regional μ receptor expression in rodents (left panel) and humans (right panel) under social comfort (green) or social distress (black) conditions. Lateralization of brain responses (right or left hemisphere) was not taken into account for simplification purpose. Pharmacological manipulations of μ receptors and modifications in μ receptor expression (in rodents) or availability (humans) affect similar brain regions, independently from the social context. These structures mostly belong to the reward circuitry (highlighted in orange). ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; AMG, amygdala; AOB, accessory olfactory bulb; BNST, bed nucleus of stria terminalis; CC, cingulate cortex; IC, insular cortex; GP, globus pallidus; LC, locus coeruleus; LS, lateral septum; MCC, middle cingulate cortex; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; POA, preoptic area of hypothalamus; PVN, paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus; Th, thalamus.
