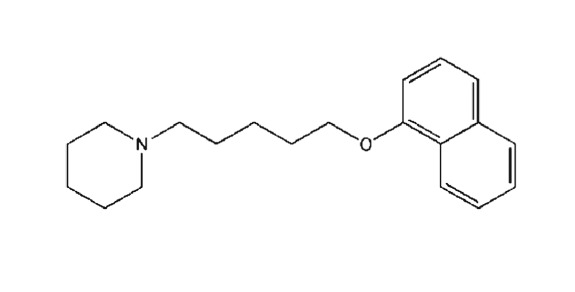
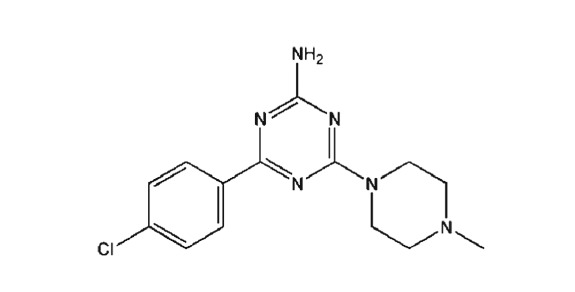
Table 1.
Structures and in vitro pharmacological profiles of E‐162 and TR‐7 in binding and functional assays (cAMP) at human H3 receptors, H4 receptors, and H1 receptors
| In vitro assays | Compounds | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| E‐162 | TR‐7 | ||
|
|
|
||
| H3R | Binding assay | K i = 55 ± 15 nMa | K i = 13 200 ± 800 nMa |
| Functional cAMP assay | IC50 = 165 nMb | nt | |
| H4R | Binding assay | K i = 58 500 ± 6600 nMc | K i = 203 ± 65 nMe |
| Functional cAMP assay | nt | IC50 = 512 nMf | |
| H1R | Binding assay | K i = 1824 ± 203 nMd | nt |
| Functional assay in guinea pig ileum | nt | pA2 = 6.3g | |
nt, not tested.
[3H]N α‐Methylhistamine binding assay performed with cell membrane preparation of HEK293 cells stably expressing the human histamine H3 receptor. Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments.
cAMP accumulation assay in HEK293 cells expressing human histamine H3 receptors, co‐treated with forskolin, (R)‐(−)‐α‐methylhistamine and the tested compound.
[3H]Histamine binding assay in membrane preparations of CHO cells stably expressing the human histamine H4 receptor. Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments.
[3H]Pyrilamine binding assay performed with CHO‐K1 cells stably transfected with the human H1 receptor. Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments.
[3H]Histamine binding assay performed with membrane preparation of Sf9 cells expressing the human H4 receptor, co‐expressed with G‐protein Gαi2 and Gβ1γ2 subunits (data from Łażewska et al., 2014).
cAMP accumulation assay in CHO cells expressing the human H4 receptor, co‐treated with forskolin, histamine and the tested compound (Łażewska et al., 2014).
Data from Mogilski et al. (2017).