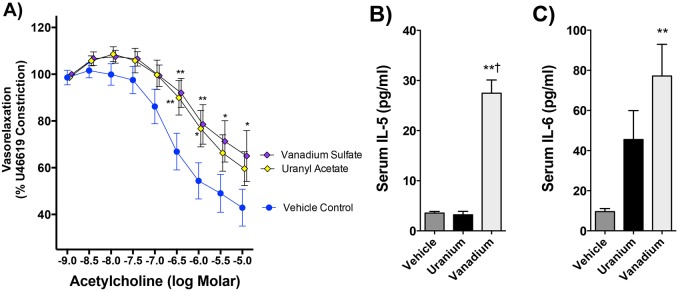
Figure 8.
Vasoreactivity and serum cytokine effects of pulmonary uranium and vanadium exposure. Acetylcholine-mediated relaxation was impaired following pharyngeal aspirations with 0.22 µmols U and V in 50 µl vehicle (A). Values are statistically significant at p < .05. *p < .05 and **p < .001 by 2-way ANOVA, N = 6 per group. Only pulmonary exposure to V induced both IL-5 (B) and IL-6 (C) levels in the circulation. No other cytokines measured in serum (see Materials and Methods) showed any significant change compared with control. **p < .001 compared with control and †p < .01 compared with uranium by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, N = 6 per group.