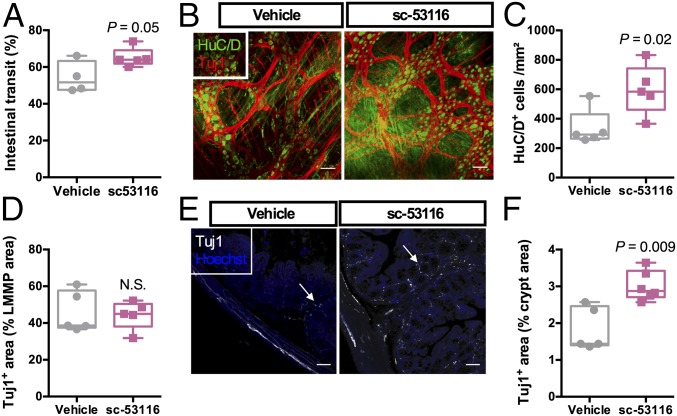
Fig. 6.
5-HT4R regulates ENS anatomy and function in GF mice. (A) Intestinal transit in GF mice that were given the 5-HT4R antagonist sc-53116 or a vehicle solution. P = 0.05; Student’s unpaired t test. (B) Representative images of the colonic LMMP of the aforementioned mice showing the pan-neuronal marker HuC/D (green) and neuron-specific β-III tubulin (Tuj1, red). (C and D) Quantification of HuC/D+ cells (C) and the Tuj1+ area (D). (E) Representative images of the innervation of the colonic crypts of the mice (white arrows) using the peripheral neuronal marker Tuj1. (F) Quantification of the Tuj1+ area. P values were determined by the Mann–Whitney test. N.S., not significant. (Scale bars: 50 µm.)