FIG. 1.
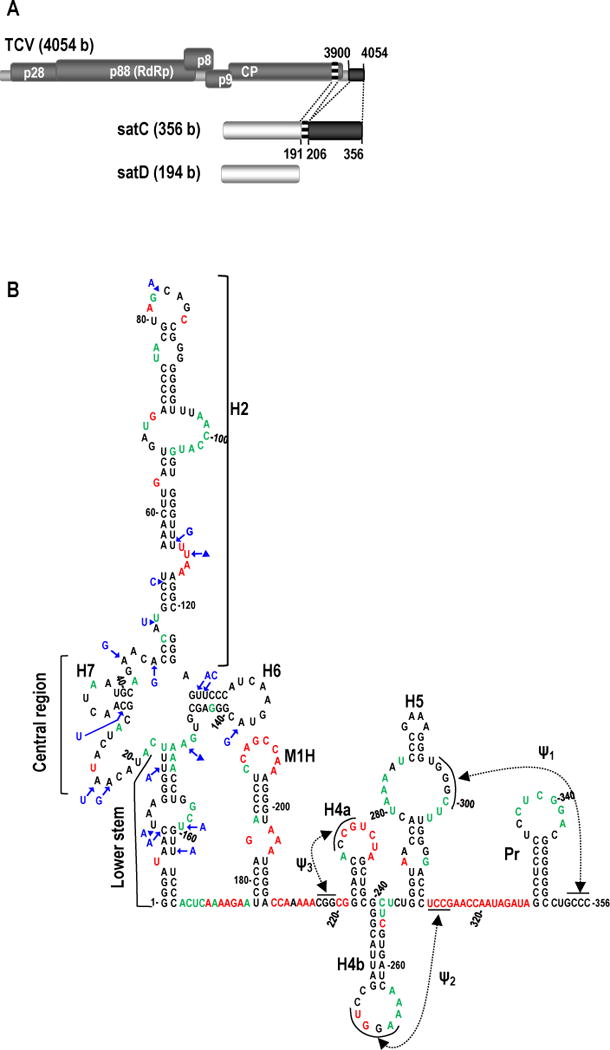
Origin and structure of TCV satC. (A) Top, TCV gRNA is 4054 bases (b) and contains five open reading frames. Replication is mediated by p28 and the RdRp readthrough protein, p88. Cell-to-cell movement is controlled by p8 and p9 (translated from a subgenomic RNA, not shown). CP (translated from a second subgenomic RNA, not shown) encodes the coat protein. Middle, the 356 b satC is composed of nearly all of the 194 b satD RNA (bottom) and two regions from the TCV 3′ end as illustrated by similar shading/patterns and the dotted lines between TCV and satC (Simon and Howell, 1986). (B) Model of wt satC structure as determined by SHAPE and mFold computational predictions. Nucleotides in red are strongly flexible; nucleotides in green are moderately/weakly flexible. Location of the lower stem (nt positions 1-17 and 150-166), central region (positions 18-47 and 124-149), and H2 region (positions 48-123) in the 5′ portion of satC are indicated. Blue residues denote how satD differs from satC in the extended hairpin region.
