Fig. 1.
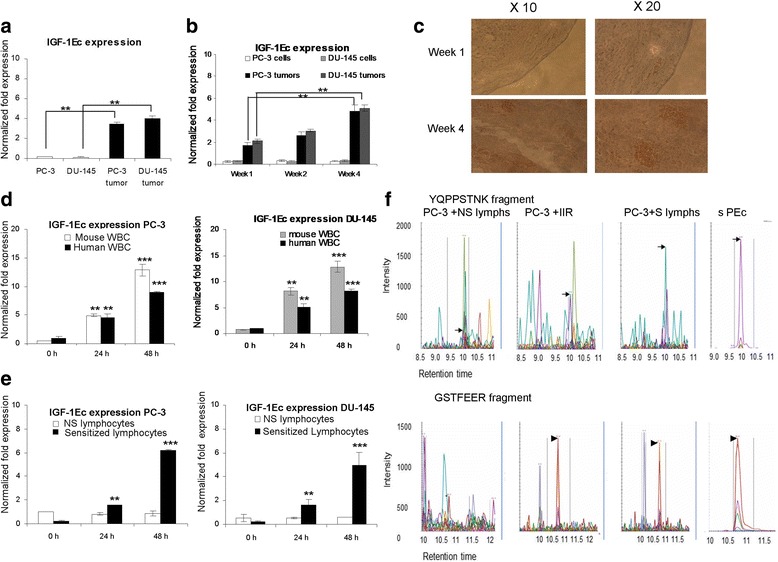
PEc expression is induced in prostate cancer cells as a response to the immune system attack. a: Analysis of IGF-Ec expression in PC-3 and DU-145 cell lines and their corresponding tumors in SCID mice, by qRT-PCR. The PC-3 and the DU-145 tumors produced significantly higher IGF-1Ec expression when compared to their corresponding cell lines. b: Analysis of IGF-1Ec expression in PC-3 and DU-145 tumors (qRT-PCR) at different time intervals. In both cases IGF-1Ec expression is increased as tumor progresses. c: Detection of mouse CD-45 positive cells in human tumors extracted from SCID mice (IHC). A significant increase of CD-45 cells was observed as tumor progresses. d: Effect of the mouse and human cells of the IIR in the IGF-1Ec expression levels in PC-3 and DU-145 cells. In both cases human and mouse IR seems to be associated with significant IGF-1Ec upregulation in prostate cancer cells at 24 and 48 h. e: Co-incubation of PC-3and DU-145 cells with human sensitized lymphocytes indicated a significant increase of the IGF-1Ec expression at 48 h compared to the prostate cancer cells treated with non-sensitized lymphocytes. f: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) analysis of protein in the media obtained from co-cultures of PC-3 cells with human lymphocytes or with cells of the IIR. Both PEc specific digest products (YQPPSTNK and GSTFEER), were detected into the media of PC-3 cells after co incubation with either the human cells of the IIR (sample 2) or with sensitized lymphocytes (sample 3) (**: p < 0.005, ***:p < 0.0005)
