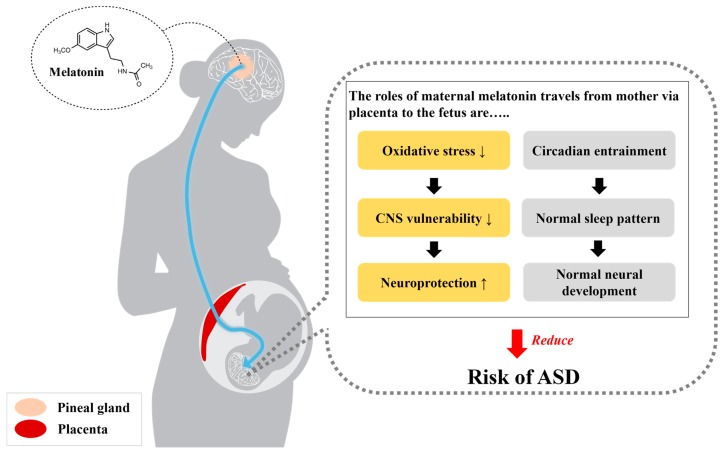
Figure 2.
The beneficial roles of maternal melatonin that travels from mother via placenta to the fetus. The functions of melatonin in neuroprotection and circadian entraining may reduce the risk of ASD. Normal melatonin concentrations during pregnancy contribute to neuroprotection and the normal neurodevelopment of the fetus through the inhibition of excessive oxidative stress in the vulnerable central nervous system. Additionally, as adequate melatonin levels maintain the normal sleep pattern and circadian rhythm, normal melatonin secretion may also elicit neurodevelopment.