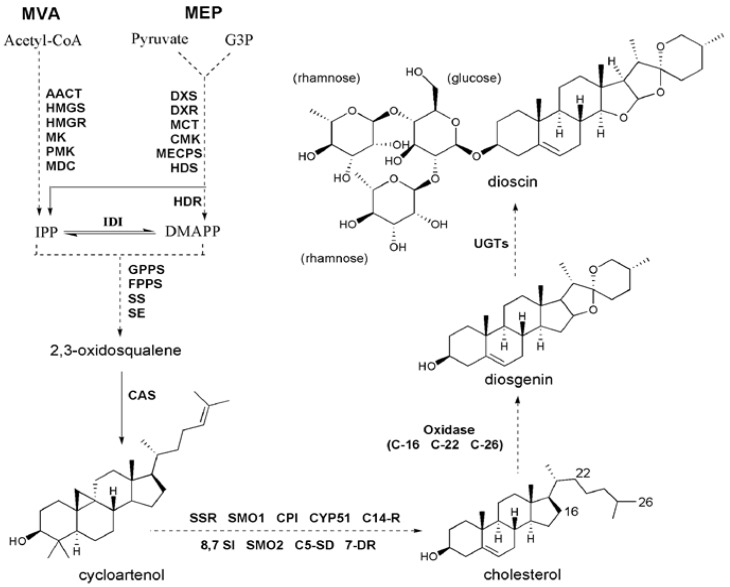
Figure 1.
Putative pathway for dioscin biosynthesis in D. zingiberensis. Abbreviations used are: AACT, acetyl CoA acetyltransferase; HMGS, hydroxymethyl glutaryl CoA synthase; HMGR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase; MK, mevalonate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; MDC, mevalonate diphosphosphate decarboxylase; IPI, IPP diphosphateisomerase; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; MCT, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyl transferase; CMK, 4-diphospho-cytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; MECPS, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2, 4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-(E)-enyl diphosphate synthase; HDR, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyldiphosphate reductase; GPPS, geranyl diphosphate synthase; FPPS, farnesyl diphosphate synthase; SS, squalene synthase; SE, squalene epoxidase; CAS, cycloartenol synthase; SSR, sterol side chain reductase; SMO1, sterol 4a–methyl oxidase 1; SMO2, sterol 4a-methyl oxidase 2; CPI, cycloeucalenol cycloisomerase; CYP51, sterol C-14 demethylase; C14-R, sterol C-14 reductase; 8,7-SI, sterol 8,7-isomerase; C5-SD, sterol C-5(6) desaturase; 7-DR, 7-dihydrocholesterol reductase.