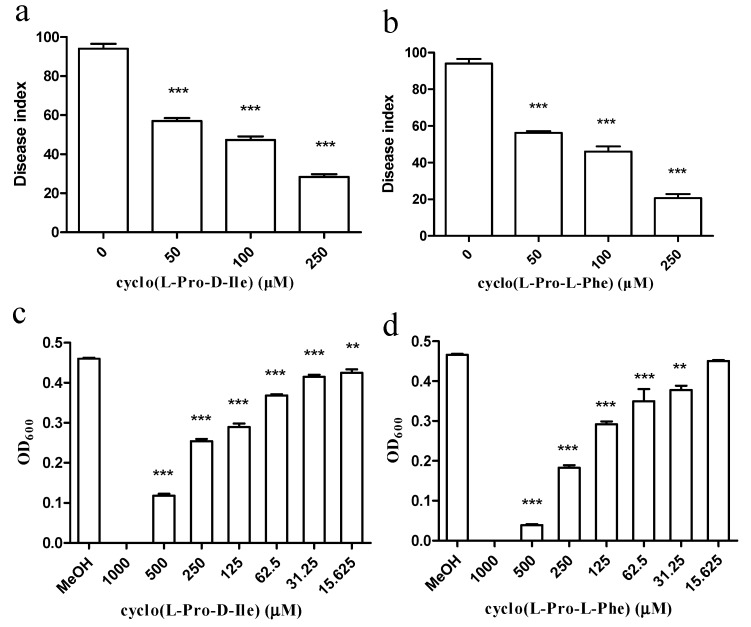
Figure 6.
Influence of cyclo(l-Pro-d-Ile) and cyclo(l-Pro-l-Phe) on R. solanacearum. The disease index of the plant infected by R. solanacearum with treatment of cyclo(l-Pro-d-Ile) (a) and cyclo(l-Pro-l-Phe) (b); antimicrobial activity of cyclo(l-Pro-d-Ile) (c) and cyclo(l-Pro-l-Phe) (d) against R. solanacearum were measured. Data are means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 (unpaired t-test).