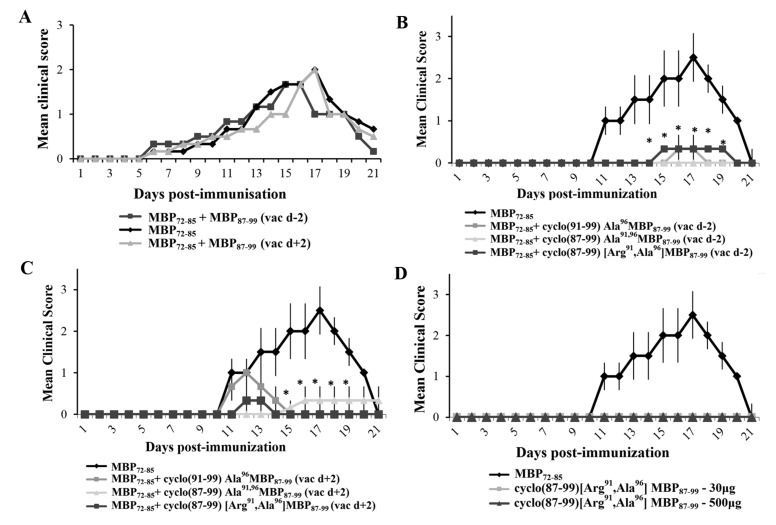
Figure 1.
Administration of cyclic myelin basic protein (MBP) 87–99 peptide analogues using prophylactic or therapeutic protocols ameliorates the development of MBP72–85-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in female Lewis rats. (A) Mean clinical scores of MBP72–85-EAE in groups of rats that were treated subcutaneously (s.c.) with wild type linear MBP87–99, as control, either 2 days before (prophylactic) or 2 days after (therapeutic) immunization with MBP72–85 (30 μg) for the induction of EAE (n = 3 for each group); (B,C) Mean clinical scores of MBP72–85-EAE in groups of rats that were treated s.c. with either cyclo(91–99)[Ala96]MBP87–99, cyclo(87–99)[Ala91,96]MBP87–99 or cyclo(87–99)[Arg91, Ala96]MBP87–99 (500 μg), either two days before (B) or two days after (C) immunization with MBP72–85 (30 μg) for the induction of EAE (n = 3 for each group); (D) Mean clinical scores of EAE in groups of rats that were immunized with MBP72–85 or cyclo(87–99)[Arg91, Ala96]MBP87–99 (at 30 μg and 500 μg), emulsified in complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) for the induction of EAE (n = 3 for MBP72–85; n = 3 for cyclic analogue). Data are from one (A,D, and experiments using cyclo(91–99)[Ala96]MBP87–99 and cyclo(87–99)[Ala91,96]MBP87–99), or one representative (experiment 1) of three (experiments using cyclo(87–99)[Arg91, Ala96]MBP87–99), independent experiments (total animals used: experiment 1, n = 24; experiment 2, n = 18; experiment 3, n = 12). Statistical significance after multigroup comparisons, using the Mann–Whitney test, is shown (*, p < 0.05).