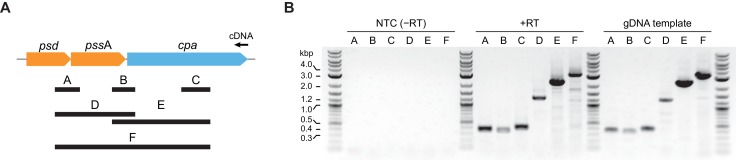
Figure 8. The cpa gene is co-transcribed together with neighboring psd and pssA genes.
(A) Organization of the cpa gene locus in Msm and design of probes used to test for gene co-transcription. (B) Visualization of all six probes amplified from cDNA produced from total RNA using a cpa-specific primer (middle of the gel). A set of reactions without reverse transcriptase was included to test for presence of contaminating genomic DNA (NTC – no template control; left part of the gel) as well as standard PCR with genomic DNA as a template to visualize the expected length of all probes (right part of the gel).