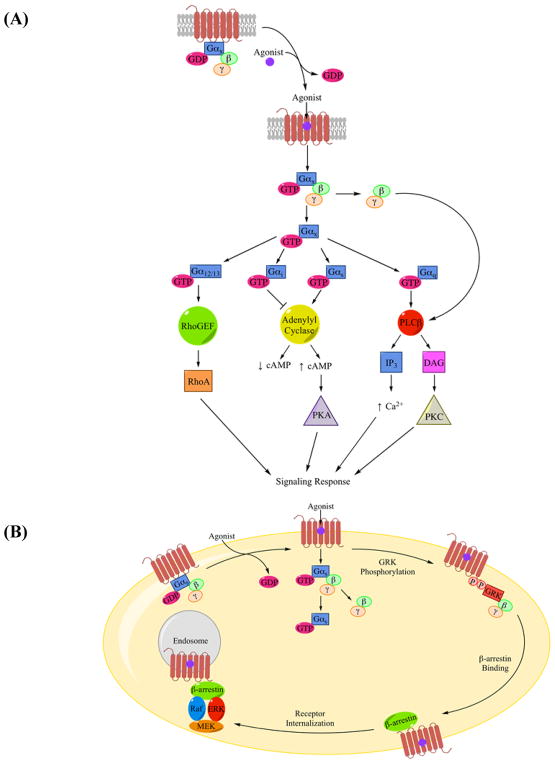
Figure 2.
(A) A classical example of GPCR signaling pathway. Receptors, such as ADRB2, are in an inactive state until an agonist binds to activate the receptor. The activated receptor-G protein complex is formed resulting in GDP to GTP exchange by the G protein complex followed by the dissociation of the Gα subunit from the Gβγ dimer. Both Gα and Gβγ subunits, in turn, activate downstream effectors. Gαx represents the general Gα subunit followed by diagrams for Gα12/13, Gαi, Gαs, and Gαq pathways. (B) β-arrestins can function as adaptor/scaffolding molecules activating the ERK (MAPK) cascade. GRK phosphorylates the activated receptor recruiting β-arrestin to the phosphorylation sites along with Raf, ERK (MAPK), and MEK. This association triggers activation of the ERK (MAPK) cascade leading to cytosolic signaling pathways. Figures 2A and 2B were adapted from Pierce, et al. [4].