Figure 1.
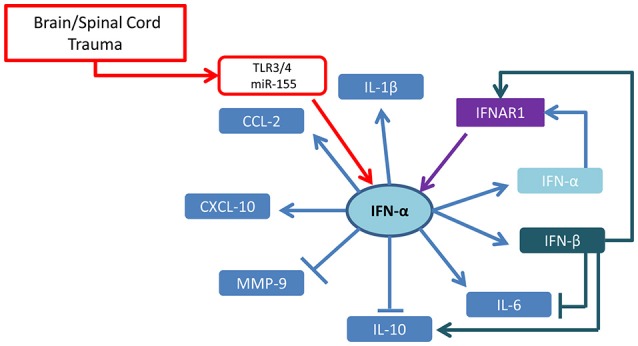
Cytokine network regulated by type-I IFN in brain and spinal cord trauma. Taking into account available evidence based on KO mice and IFN administration in brain and spinal cord injury, the emerging picture shows that IFN-α upregulates its own expression and the expression of IFN-β through the IFNAR receptor and induces CXCL10 and CCL2 chemokines as well as IL-6 and IL-1β. While IFN-α appears to downregulate IL-10, IFN-β administration results in the upregulation of this anti-inflammatory cytokine.
