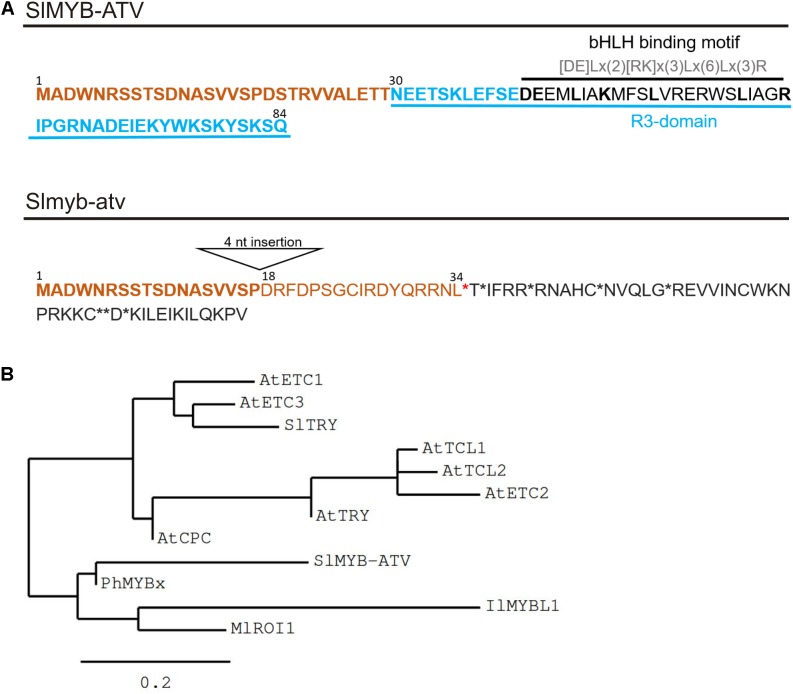
FIGURE 3.
Main features of the SlMYB-ATV mutated protein. (A) Predicted protein sequences as result of the translation of the wild type (wt) allele (SlMYB-ATV) and of the atv allele (Slmyb-atv) of Solyc07g052490. N-terminal common aminoacids are marked in bold orange. In the wt version of the polypeptide, the R3 domain, containing the bHLH interaction motif, is indicated. In the atv version of the protein the position of the 18th amino acid, the first different from wt due to the 4 nucleotide (nt) insertion in the corresponding gene, is indicated. Stop codons are indicated by asterisks. (B) Phylogenetic tree showing the relatedness of SlMYB-ATV with other known plant R3-MYB proteins. The analysis was performed on the phylogeny.fr platform (Dereeper et al., 2008), using the maximum likelihood method (PhyML Program) and reliability for internal branch was assessed using the aLRT test (SH-Like). Graphical representation of the phylogenetic tree was performed with TreeDyn. Protein sequences were identified on the NCBI website and the relative GeneBank accession numbers are as follows: AtETC1 (OAP16560), AtETC2 (Q84RD1), AtETC3 (NP_192015), AtTCL1 (D3GKW6), AtTCL2 (B3H4X8), AtCPC (BAA21917), AtTRY (Q8GV05), SlTRY (MF197521), SlMYB-ATV (MF197509), PhMYBx (AHX24371), IlMYBL1 (ASR83103.1), MlROI1 (AGC66791.1).