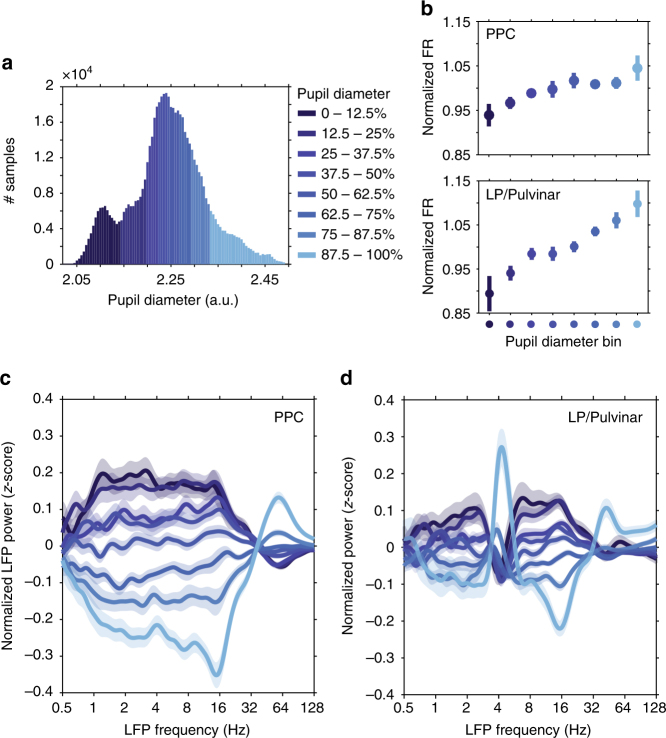
Fig. 2.
Neuronal spiking rate and LFP spectral power in PPC and LP/Pulvinar are modulated with pupil diameter. a A representative example of how pupil diameter time series were divided up into bins (each bin represents 12.5% of all samples). Neurophysiological data were then analyzed according to pupil diameter bin. b The normalized spiking rate in both PPC and LP/Pulvinar increases with pupil dilation. Color denotes pupil diameter, as indicated in a. c The mean (±SEM) z-scored LFP power in PPC as a function of carrier frequency across pupil diameter bins. Low (<30 Hz) and high (>30 Hz) frequency LFP power displayed opposing relationships to pupil diameter. d the same as c but for LP/Pulvinar LFP power. Note the antagonism between low- and high-frequency LFP oscillatory power is similar to PPC, with the exception of the theta band (∼4 Hz), which displays increased power during large pupil diameter states