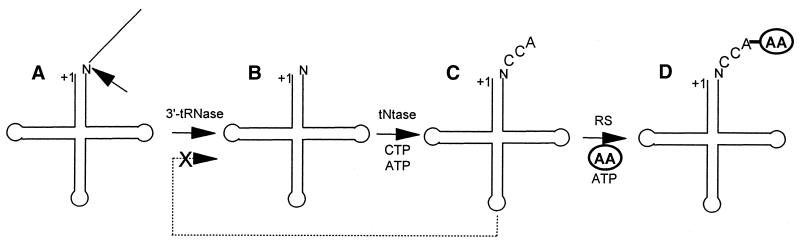
Figure 1.
Eukaryotic tRNA end processing from the 3′-tRNase reaction through aminoacylation. The tRNA has been processed by RNase P to +1. (A) The RNase P product is a substrate for 3′-tRNase (←). N, discriminator base. (B) The 3′-tRNase product is a substrate for CCA addition by tRNA nucleotidyltransferase (tNtase). (C) The tNtase product (mature tRNA) is a substrate for aminoacylation by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (RS). (D) Charged tRNA. The dashed arrow from (C) to (A, B) with an X through it signifies that mature tRNA with CCA at its 3′-end is a 3′-tRNase anti-determinant (8); it is neither a substrate nor a good inhibitor.