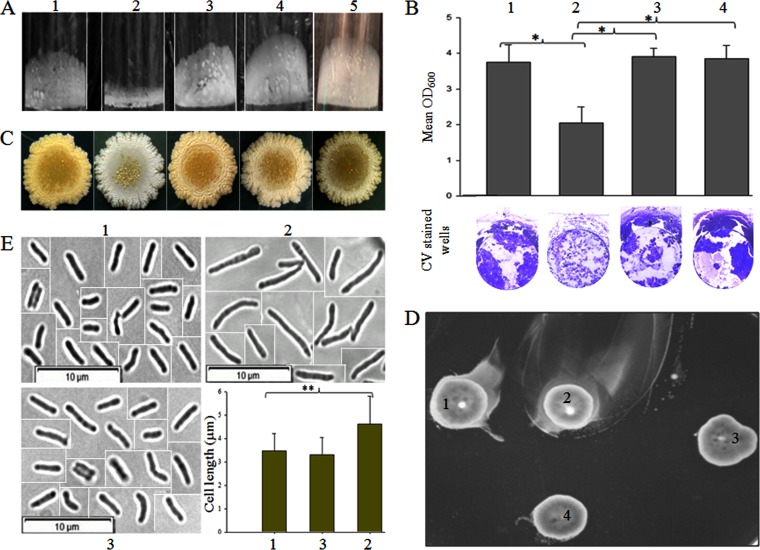
FIG 5.
Effect of double deletion on the phenotype of M. smegmatis mc2155. Numbers 1 to 5 represent strains mc2155, Δms33/32, Δms33/32::pM33, Δms33/32::pM11, and Δms33/32::pM32, respectively. (A) Pellicle formation of the different strains. (B) Quantitative analysis of the biofilm formation from six replicates (means ± SDs). The lower panel shows the representative images of the crystal violet (CV)-stained biofilms in the well. (C) Colony morphology of the strains on an LB agar plate. (D) Motility of the strains on an M63 plate containing 0.3% agarose. We refer the motility of the double-knockout mutant, Δms33/32, as hypermotility. (E) Cell shape and cell length analysis by phase-contrast microscopy (picked from the three different focuses) at a magnification of ×100. As all the cells were not present in the same field during microscopy, the cropped and separate images of the individual cells are presented here together with demarcated boundaries. The bar graph shows the cell length measurement (mean ± SD; 100 cells/strain). The asterisks in both the bar graphs (B and E) indicate the statistical significance (P < 0.001), calculated using the Bonferroni t test of one-way ANOVA.