Figure 1.
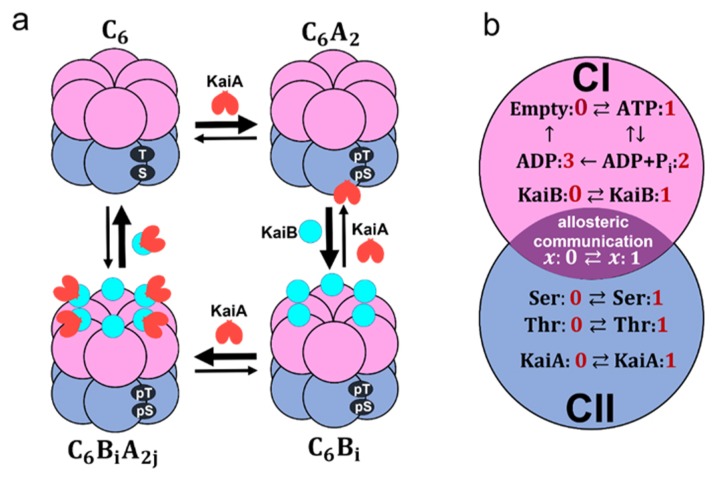
Coarse-grained models of the KaiABC system. a) Schematic of interactions among Kai proteins considered in the MM model. Two phosphorylation sites, Ser431 and Thr432, of each subunit in the CII domain (blue) are repeatedly phosphorylated (pS, pT) and dephosphorylated (S, T). KaiA dimer (red) binds to KaiC hexamer C6 to form C6A2. The CI (pink) of each subunit binds to KaiB (cyan) to form C6Bi with 1 ≤ i ≤ 6, which further binds to KaiA dimers to form C6BiA2j with 1 ≤ j ≤ i. b) Reactions and states in a KaiC subunit in the SM model. ATP hydrolysis reactions and KaiB binding/dissociation reactions occur in the CI domain (pink). Phosphorylation (P)/dephosphorylation (dP) reactions and KaiA binding/dissociation reactions take place in the CII domain (blue). CI and CII domains are coupled through allosteric structural change.