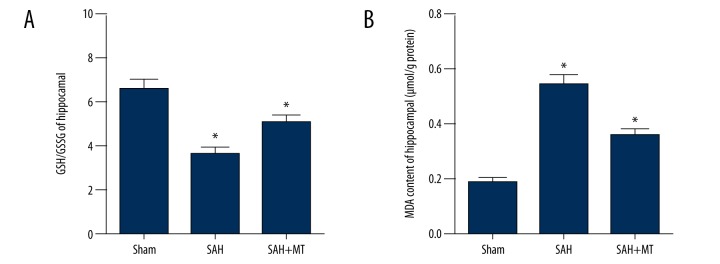
Figure 5.
Melatonin treatment upregulated SIRT3 expression caused by oxidative stress in the brain following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Three mouse groups were studied: the subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) group; the sham group; and the SAH + melatonin-treated group (intraperitoneal dose, 150 mg/kg). (A) Reduced glutathione (GSH), and its ratio with oxidized glutathione (GSSG) (the GSH: GSSG ratio) was inhibited in the SAH group, and melatonin treatment partially reversed the change in GSH: GSSG ratio induced by SAH. (B) Malonaldehyde (MDA) was significantly increased in the SAH group; MDA was significantly suppressed following treatment with melatonin.