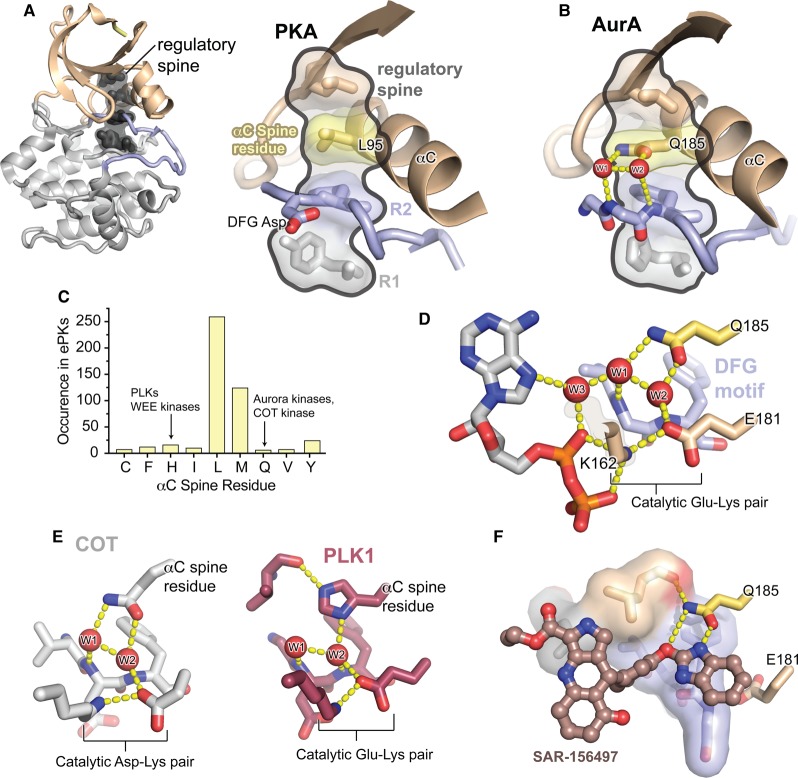
Figure 2. The unusual regulatory spine of AurA contains a functionally important water-mediated allosteric network.
(A) Left: Structure of the kinase domain core of PKA, colored as in Figure 1, with the four residues of the regulatory spine highlighted in dark gray. Right: Enlarged view of the regulatory spine of PKA, with the αC spine residue highlighted in yellow. (B) Enlarged view of the regulatory spine of AurA, colored as in (A), showing the interactions of the unusual Q185 αC spine residue with structured water molecules (red) co-ordinated to the DFG motif in the active site. (C) Histogram showing the frequency of different amino acid residues at the αC spine position across all ePKs. Values are derived from the original multiple sequence alignments published by Manning et al. [24]. (D) View of the water network in the AurA active site (PDB ID: 5G1X), showing the Q185 residue, three water molecules, the Glu-Lys salt bridge, and the bound ADP molecule. (E) Left: View of the active site of COT kinase showing the similar interactions of the glutamine αC spine residue with the active site water molecules (PDB ID: 4Y85). Right: View of the active site of PLK1 showing the water network mediated by the histidine αC spine residue (PDB ID: 2OWB). (F) Structure of SAR-156497 bound to AurA showing the interactions of the small molecule with the Q185 residue (PDB ID: 4UZD).