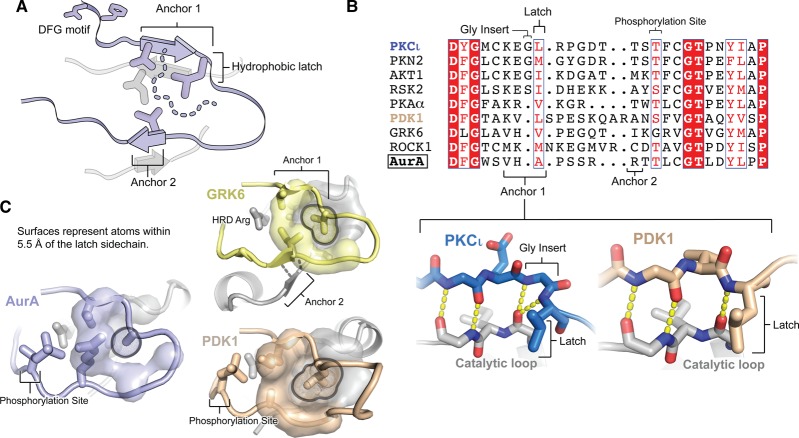
Figure 5. Defective anchoring of the AurA activation loop may underlie its heightened dynamics.
(A) Schematic representation of the activation loop of an active protein kinase, showing the DFG motif at the N-terminus, the two anchor points that stabilize the N- and C-terminal halves of the loop, and the hydrophobic latch residue at the end of Anchor point 1. The sidechains of several residues located on the anchor points and the underlying catalytic loop are shown, which form part of the interaction surface (dashed line) for the hydrophobic latch residue. (B) Sequence alignment of the activation loops of AurA and members of eight AGC kinase subfamilies. The alignment was manually curated based on X-ray structures of each kinase [PDB IDs: 4DC2 (PKCι), 4CRS (PKN2), 4EKK (AKT1), 4NW6 (RSK2), 1L3R (PKA), 4RQK (PDK1), 3NYN (GRK6), 4W7P (ROCK1), 1OL5 (AurA)]. In the lower inset, a comparison is shown of the structures of Anchor point 1 in PKCι (a kinase with a glycine insert before the hydrophobic latch residue) and PDK1 (a kinase lacking the insert), highlighting the similar positioning of the leucine hydrophobic latch residue in the two cases. (C) Crystal structures are shown highlighting the anchoring of the activation loop in AurA (blue) and the AGC kinases GRK6 (yellow) and PDK1 (beige). Atoms within 5.5 Å of the sidechain of the hydrophobic latch residue are shown in a surface representation (for clarity surfaces were excluded for the residues preceding and following the latch residue).