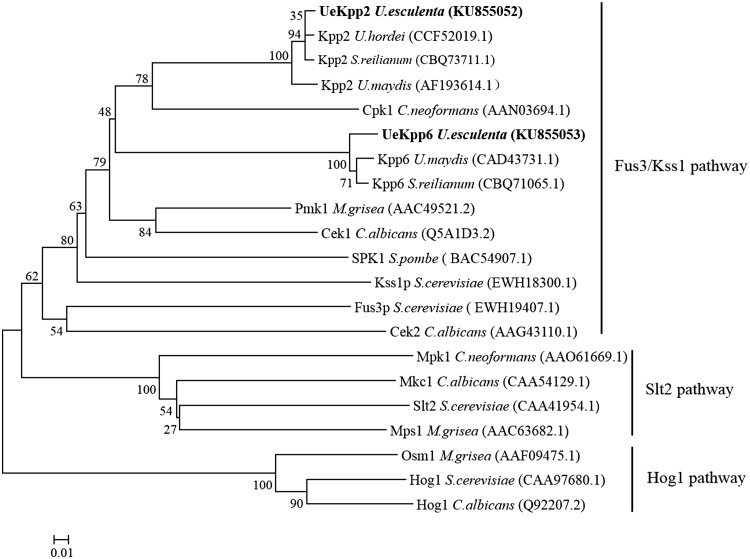
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree constructed from the MAP kinase protein sequences of several fungi. Amino acid sequences were used and analyzed by MEGA 5.0 with the neighbor-joining method. Numbers on the branches represent bootstrap support for 1000 replicates. The related MAPK proteins used were: Ustilago esculenta UeKpp2(KU855052) and UeKpp6 (KU855053), marked in bold; Ustilago hordei Kpp2 (CCF52019.1); Sporisorium reilianum Kpp2 (CBQ73711.1) and Kpp6 (CBQ71065.1); Ustilago maydis Kpp2 (AF193614.1) and Kpp6 (CAD43731.1); Cryptococcus neoformans Cpk1 (AAN03694.1) and Mpk1 (AAO61669.1); Magnaporthe grisea Pmk1 (AAC49521.2), Mps1 (AAC63682.1) and Osm1 (AAF09475.1); Candida albicans Cek1 (Q5A1D3.2), Cek2 (AAG43110.1), Mkc1 (CAA54129.1) and Hog1 (Q92207.2); Schizosaccharomyces pombe SPK1 (BAC54907.1); Saccharomyces cerevisiae Kss1p (EWH18300.1), Fus3p (EWH19407.1), Slt2 (CAA41954.1) and Hog1 (CAA97680.1)