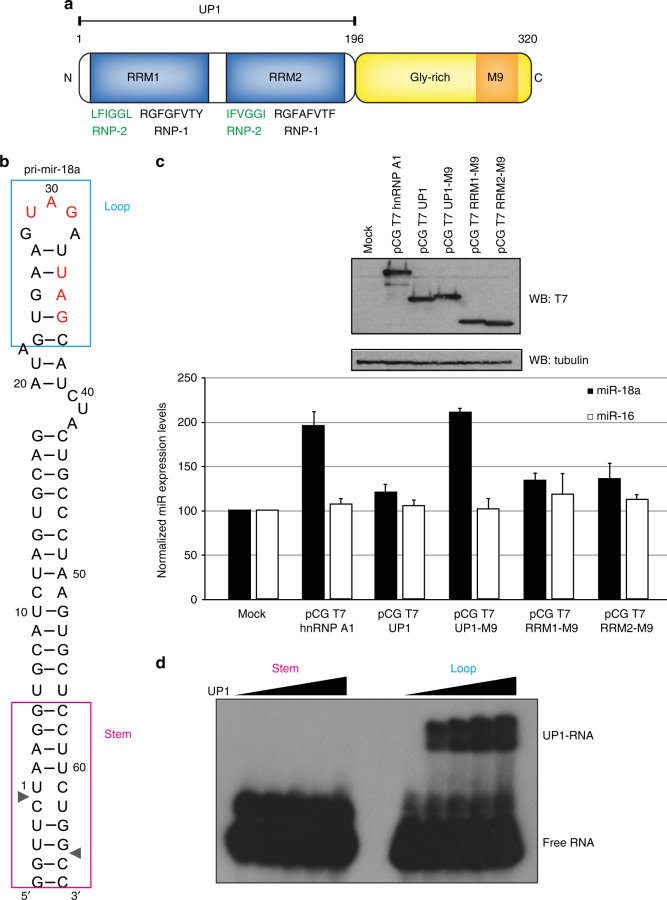
Fig. 1.
The tandem RRMs of hnRNP A1 promote pri-mir-18a biogenesis in living cells. a Domain structure of human hnRNP A1. The sequences of conserved RNP-1 and RNP-2 motifs in the RRM domains are indicated. M9 is a transport signal linked with both nuclear import and export of this protein. b Secondary structure of pri-mir-18a RNA based on footprinting analysis7. Regions corresponding to the terminal loop and stem are boxed. The cleavage sites for Microprocessor (Drosha/DGCR8) are indicated by arrowheads. c Effect of transiently transfected epitope-tagged T7-hnRNP A1, UP1, UP1-M9, RRM1-M9, and RRM2-M9 in the processing of pri-mir-18a in HeLa cells in culture. Processing of pri-mir-16 was included as a control (white bars). The upper panel shows the level of expression of T7 epitope-tagged hnRNP A1 WT or constructs expressing individual domains (RRM1 or RRM2) or the UP1 fragment (tandem RRM1-RRM2). An M9 sequence was included to direct the nuclear localization of the UP1, RRM1, and RRM2 constructs. d Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) of UP1 in complex with pri-mir-18a loop and stem RNAs