Fig. 6.
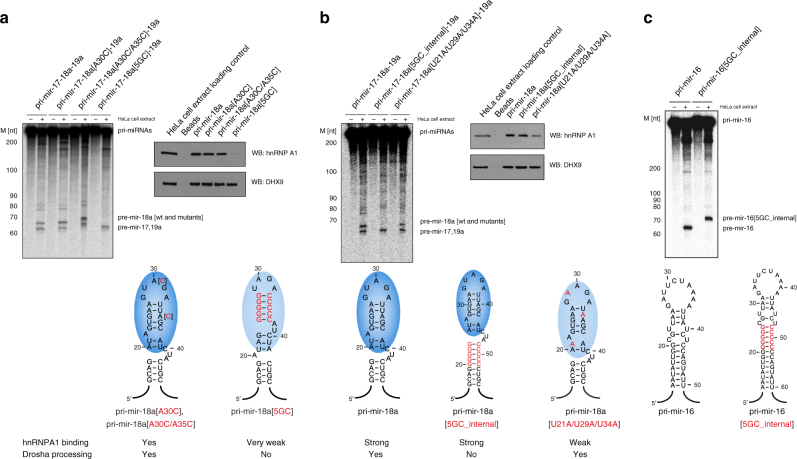
Mechanism of hnRNP A1 stimulation of pri-miRNA processing. a Pri-mir-18a with single or double A→C point mutations still bind hnRNP A1 in RNA pull-down assays and are processed by Drosha (in vitro processing assay with the pri-mir-17-18a-19a cluster, wildtype and mutants), whereas pri-mir-18a mutant with a 5GC clamp does not bind hnRNP A1 (RNA pull-down assay is shown on the right) and is not processed by Drosha. b Pri-mir-18a with a 5GC_internal clamp and wild-type terminal loop binds hnRNP A1 but is not processed by Drosha. Pri-mir-18a with triple mutations [U21A/U29A/U34A] binds hnRNP A1 with lower affinity than the wild-type pri-mir-18a but is still efficiently processed by Drosha. c In vitro processing assay of pri-mir-16 with 5GC_internal clamp shows efficient processing by Drosha, similar to pri-mir-16 wildtype