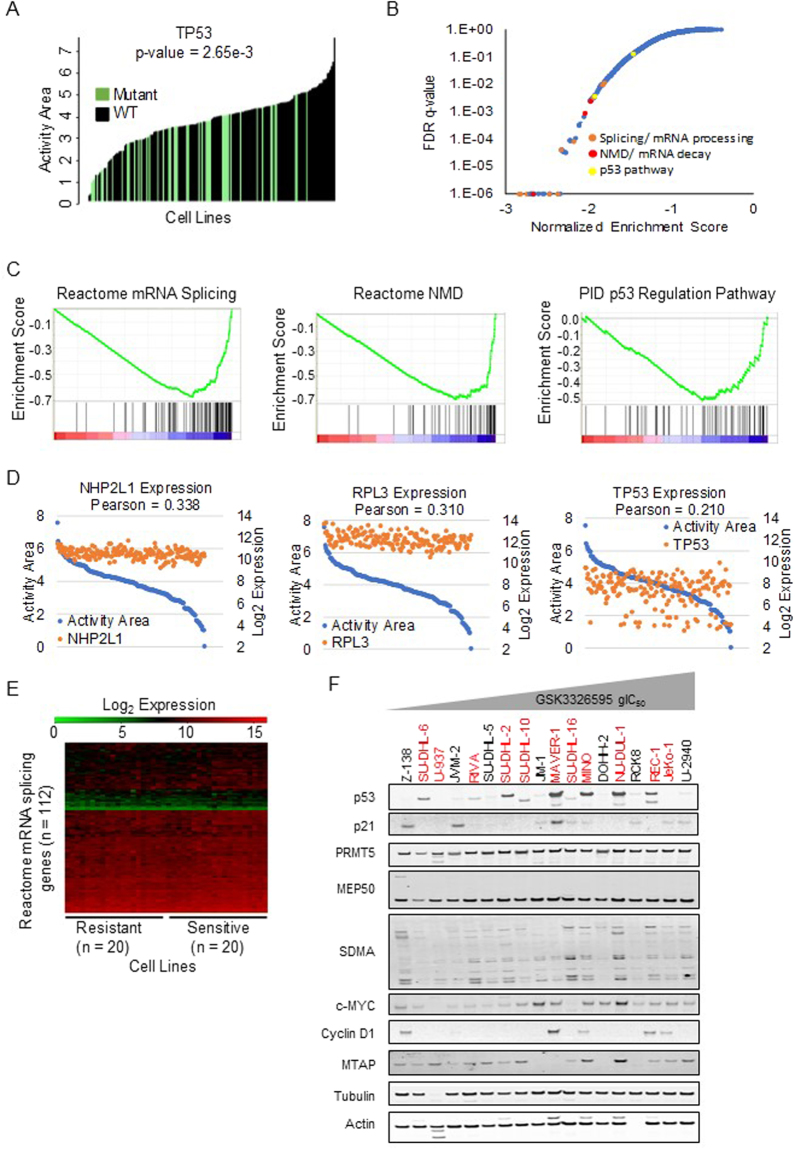
Figure 6.
p53 mutational status correlates with sensitivity to PRMT5 inhibition. (A) Correlations with activity area calculated from a 10-point dose curve 10 days post treatment with GSK3203591. TP53 mutation is one of the top predictors of resistance. (B) A pre-ranked list of Pearson correlation of gene expression with sensitivity was submitted to GSEA and the gene sets plotted by increasing FDR. (C) The lowest FDR gene set from each of the three categories of interest: Splicing, Nonsense mediated decay (NMD), and p53 pathway gene sets, are represented by enrichment plots from the GSEA outputs (top panel). The highest correlated gene by Pearson from each of the three represented gene sets is plotted by decreasing sensitivity. (bottom panel). (D) A hierarchical clustering of expression values for genes in the “Reactome_mRNA_splicing” gene set from the 20 most sensitive and resistant cell lines. (E) Western blot showing basal expression of a variety of proteins in lymphoma cell lines ranging in sensitivity to PRMT5i (most sensitive far left, least sensitive far right) and of various p53 mutational statuses. p53 mutant cell lines in red.