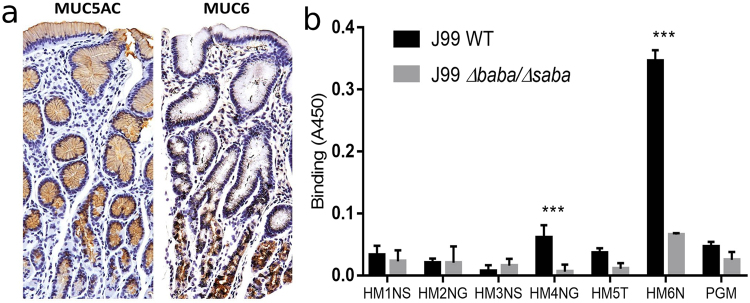
Figure 2.
Location of mucins with antibody staining. (a) Left: Surface and foveolar epithelial cells stained brown with an antibody recognizing MUC5AC. Right: gland cells stained brown with an antibody against MUC6. The sections were counterstained with heamatoxylin, outlining the tissue in blue, with the dark blue representing nuclei. (b) Binding of J99 WT and its isogenic adhesin deletion mutant J99ΔbabAΔsabA to mucins from five patients with varying glycosylation and health status (outlined in Table 1) and to pig gastric mucin (PGM). The *** indicates p < 0.001 difference in binding between J99 WT and J99ΔbabAΔsabA to a mucin (Two way ANOVA). The results are shown after subtracting the background signal for the assay in the absence of mucins. The level of binding was relatively weak in comparison to what we previously have showed for some other human mucins18, although the positive control human mucin (HM6N in the graph) displayed high binding to H. pylori, demonstrating that the low binding is not due to technical issues, but due to the properties of the mucins investigated in this study.