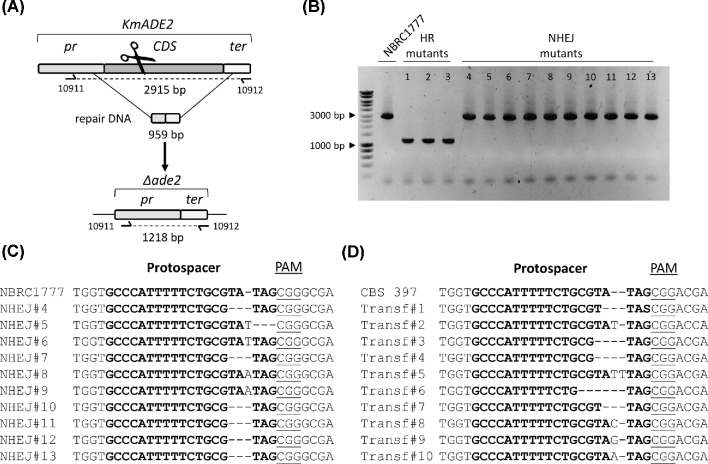
Figure 3.
Efficient gRNA targeting enables marker-free gene deletion in haploid K. marxianus NBRC 1777 and gene disruption in diploid K. marxianus CBS 397. (A) Schematic representation of the ADE2 editing upon transformation of NBRC 1777 with pUDP082 (gRNAKmADE2) and a repair DNA fragment. The primers for diagnostic PCR of transformants are indicated. (B) Diagnosis of 13 randomly picked red Ade− transformants of NBRC 1777 upon transformation with pUDP082 and a 959-bp marker-free repair fragment. Three transformants (HR mutants 1–3) showed a PCR product of 1218 bp corresponding to the deleted allele. The control labeled NBRC 1777 and 10 transformants (NHEJ mutants 4–13) showed a PCR product of 2915 bp corresponding to the wild-type allele. (C) Sanger sequencing results of purified PCR fragments from 10 Ade− mutants (corresponding to mutants 4–13 in panel B) derived from the transformation of NBRC 1777 with pUDP082 and repair fragment. (D) Sanger sequencing results of purified PCR fragments of 10 randomly picked red Ade− mutants derived from the transformation of CBS 397 with pUDP082 and repair fragment.