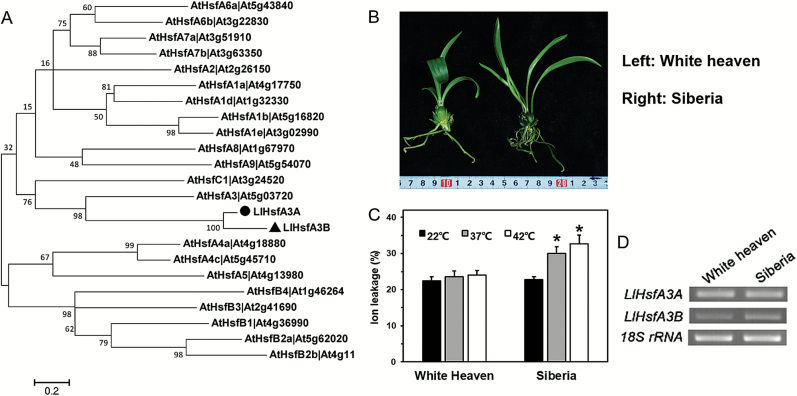
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the LlHsfA3A and LlHsfA3B proteins and RT-PCR detection of LlHsfA3A and LlHsfA3B in different lily cultivars. (A) Phylogenetic tree of LlHsfA3A and LlHsfA3B proteins and the Arabidopsis Hsf family. The amino acid sequences of the Arabidopsis Hsfs were downloaded from the TAIR website (www.arabidopsis.org). The software MEGA 5.0 was used to reconstruct the evolutionary tree. Node values are percentages of bootstraps generated with 1000 replicates. The scale bar shows an evolutionary distance corresponding to 0.2 amino acid substitutions per site. (B) Example plants of the two lily cultivars, ‘White heaven’ and ‘Siberia’. (C) Relative ion leakage of the leaves after heat stress (HS) at 37 or 42 °C for 1 h compared with the control (22 °C). Each treatment included three plants, and data are means (±SD) of three independent experiments. Significant differences compared with the control with determined using Student’s t-test (*P<0.05). (D) Detection of LlHsfA3A and LlHsfA3B in the HS transcripts of ‘White heaven’ and ‘Siberia’ using RT-PCR (32 cycles). These bands were confirmed by sequencing.