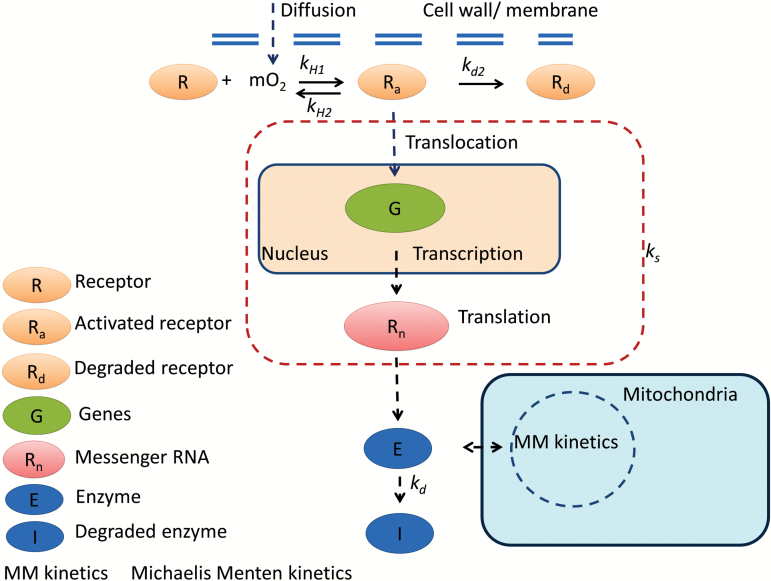
Fig. 1.
Proposed response of receptor, enzyme, and respiration to O2 level. The receptor in a pear cell was assumed to be activated by O2, and subsequently to trigger a biochemical chain involving transcription and translation steps, resulting in the final level of the enzyme E. A change in level of the enzyme E in response to the activated receptor was characterized by a lumped synthesis rate ks agglomerating multiple conversion steps in a signal transduction cascade. Solid arrows represent direct conversions, while the dashed arrows indicate more general pathway interactions containing multiple conversion steps. Reaction equations are derived and shown in Supplementary Protocol S1 and Supplementary Fig. S1.