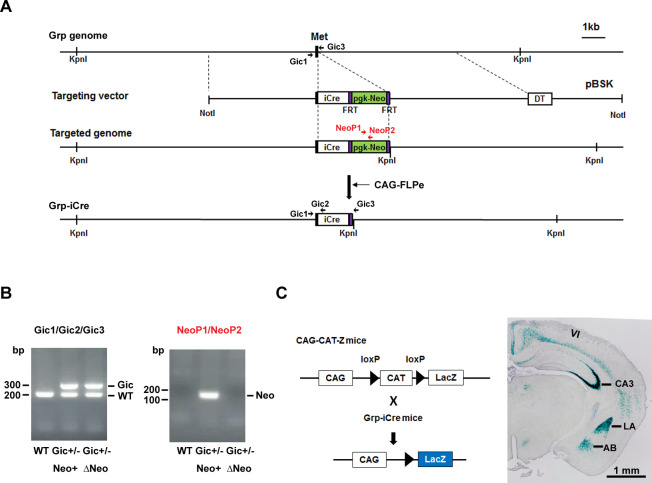
Figure 1. Generation and characterization of Grp-iCre mice.
(A) Schematic diagram of the gene targeting strategy. iCre and pgk-neo cassettes flanked by two FRT sites were inserted into the gastrin-releasing peptide gene (Grp) locus. Met is the translation initiation site of Grp. The location of PCR primers (Gic1, Gic2, Gic3, NeoP1, and NeoP2) used for genotyping are indicated. DT, diphtheria toxin gene; pBSK, pBluescriptII SK. The chimeric mouse obtained was crossed with a CAG-FLPe mouse to delete the pgk-neo cassette and establish the Grp-iCre (Gic) mouse line. (B) Genotyping PCR of genomic DNA prepared from WT; Gic+/−, Neo+; Gic+/−, and ΔNeo mice. (C) Cre activity in Grp-iCre mice was examined by crossing Grp-iCre mice with lacZ reporter mice (CAG-CAT-Z) mice. β-galactosidase expression in a Grp-iCre/CAG-CAT-Z mouse brain stained with X-gal. X-gal staining revealed robust Cre-loxP recombination in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala (LA) and the hippocampal CA3 region, with sparser recombination in the accessary basal nucleus of the amygdala (AB), and in layer 6 of the cerebral cortex (VI).