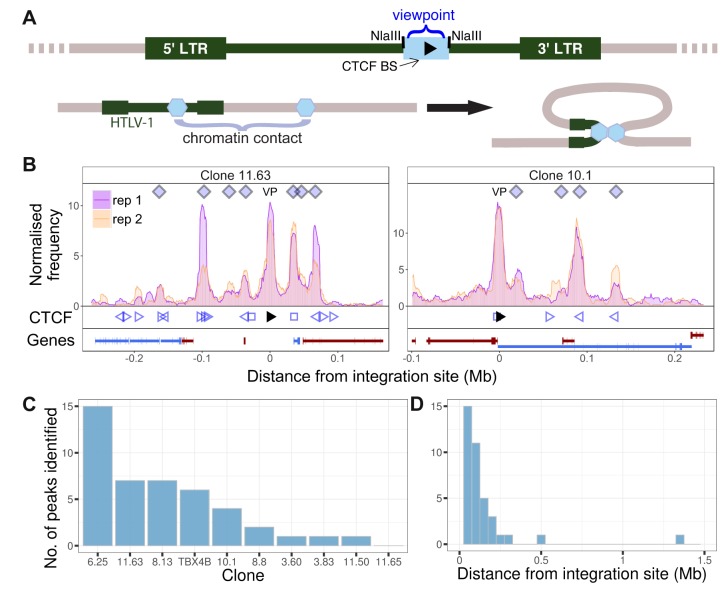
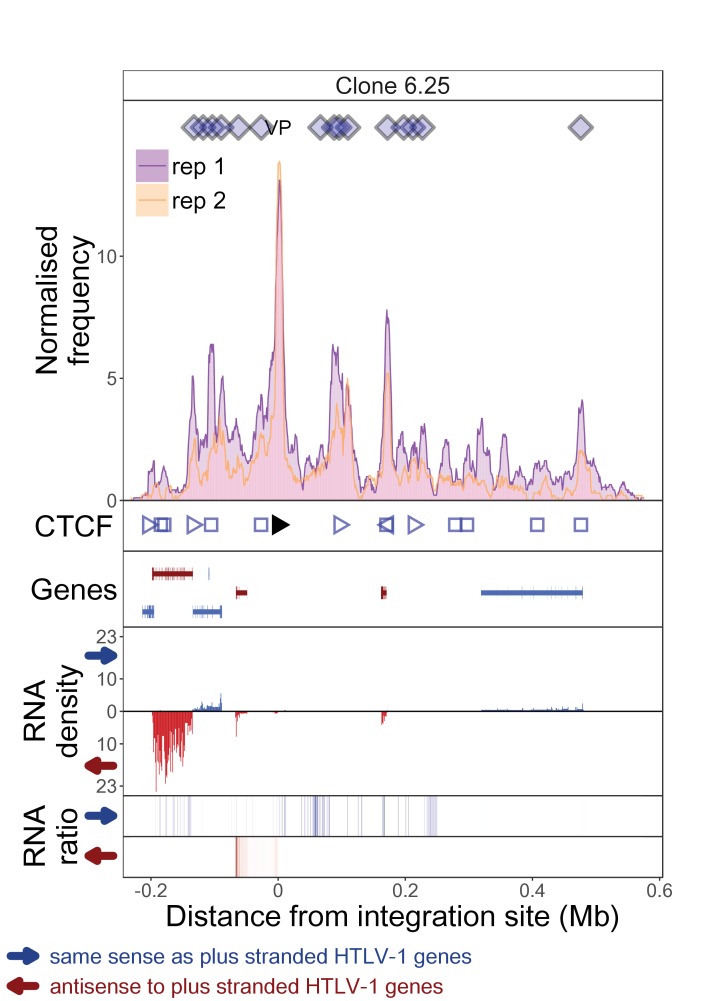
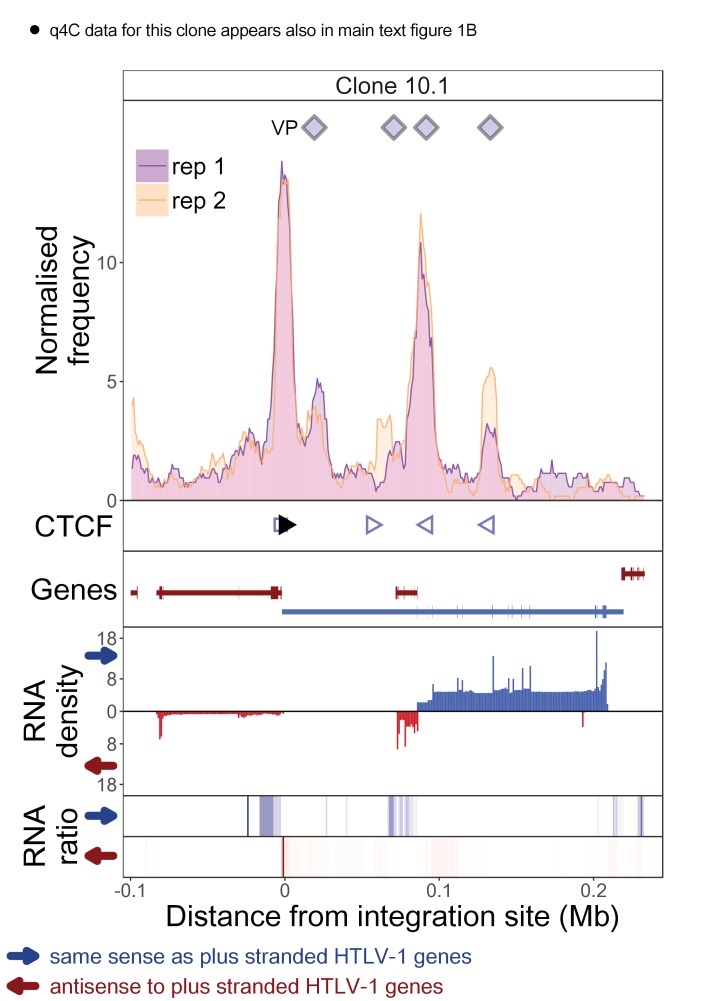
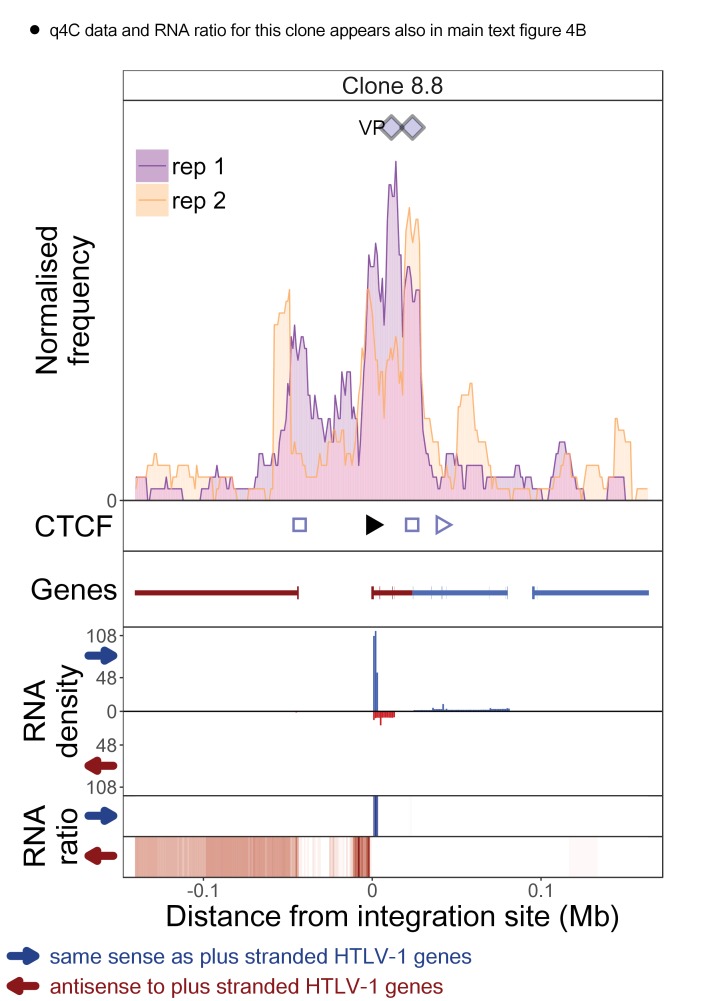
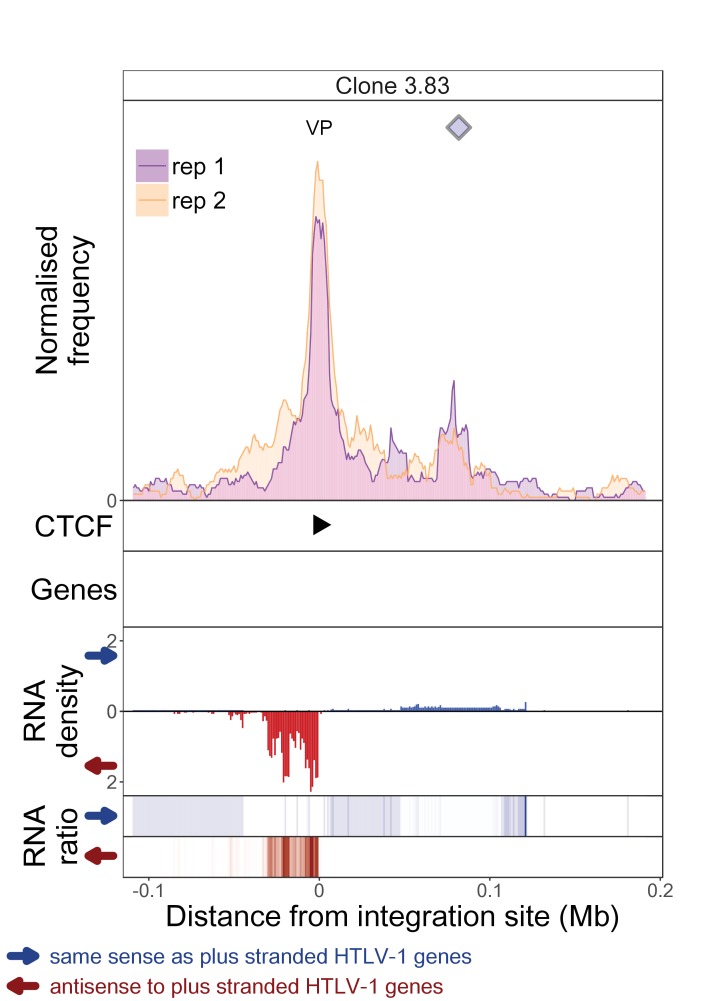
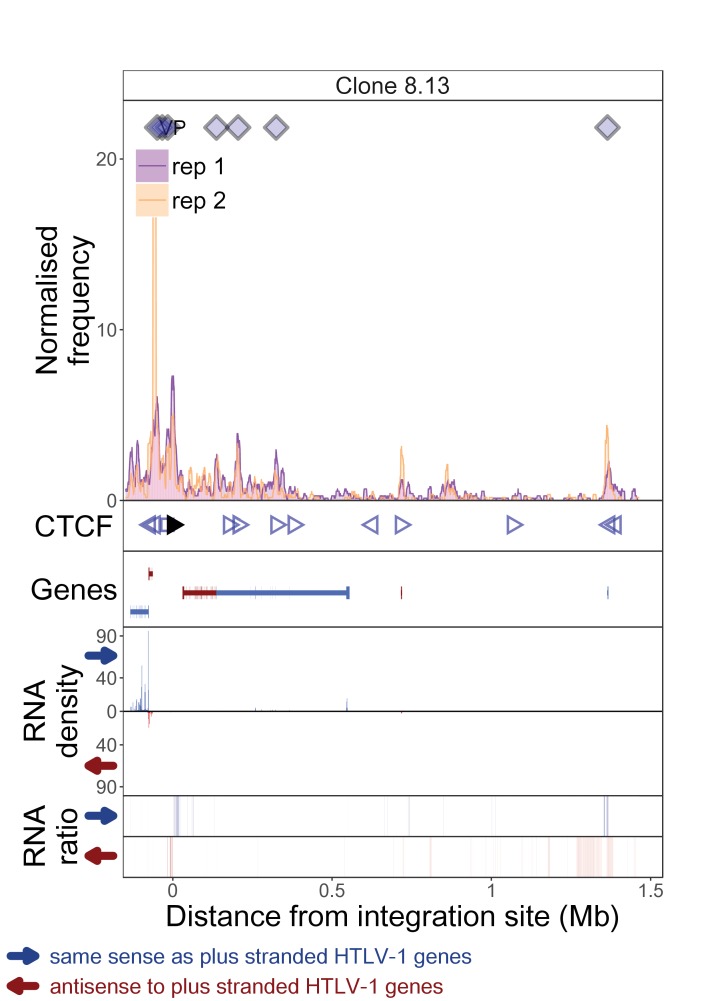
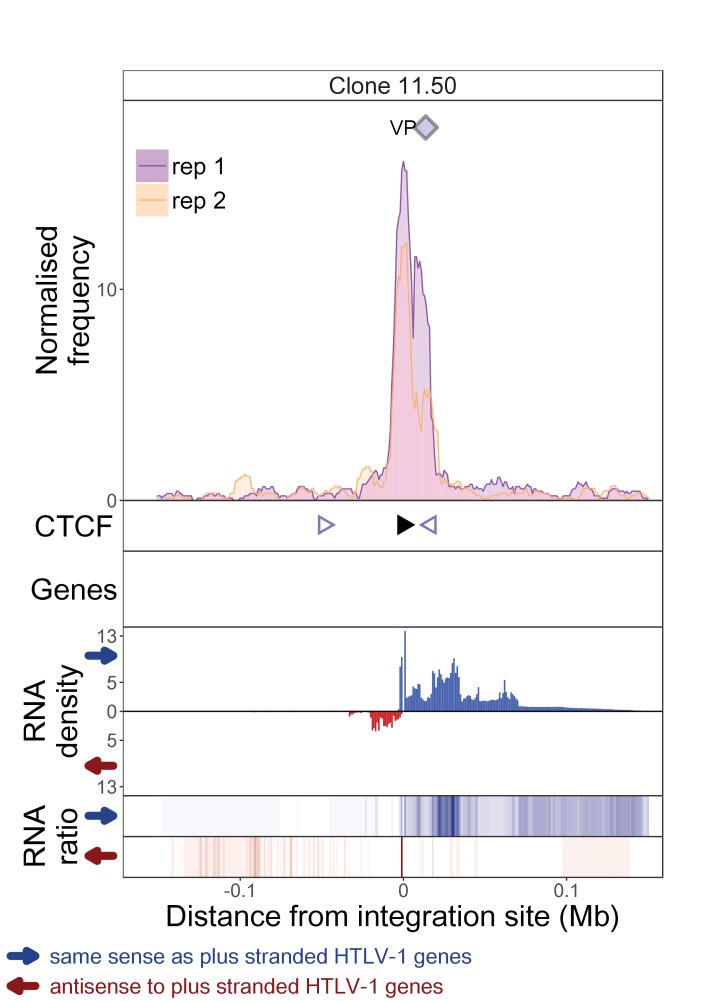
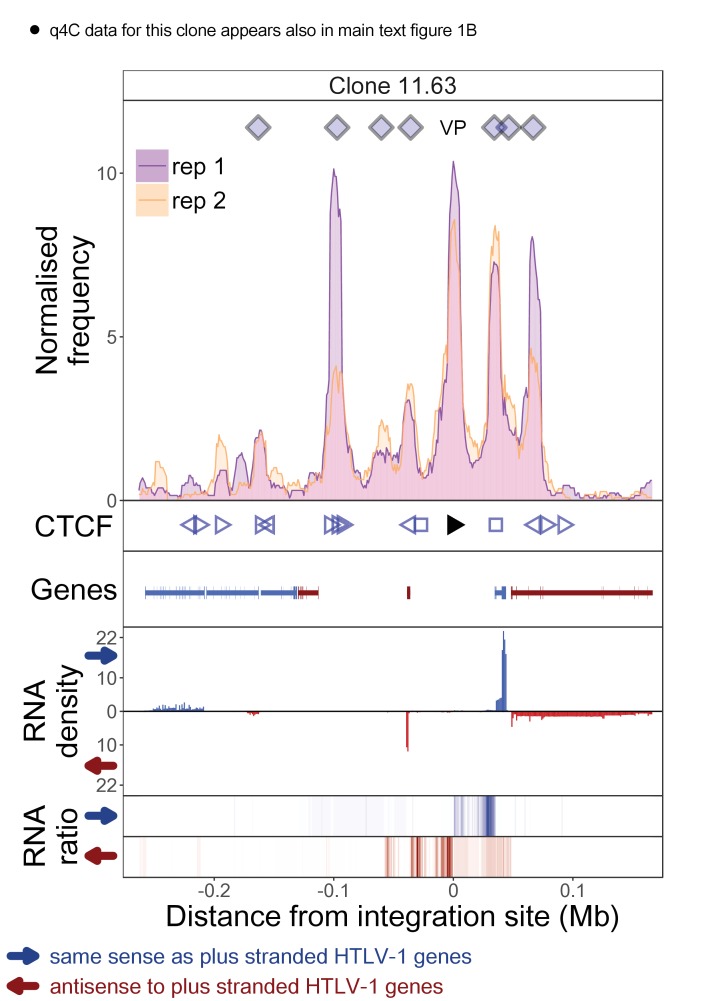
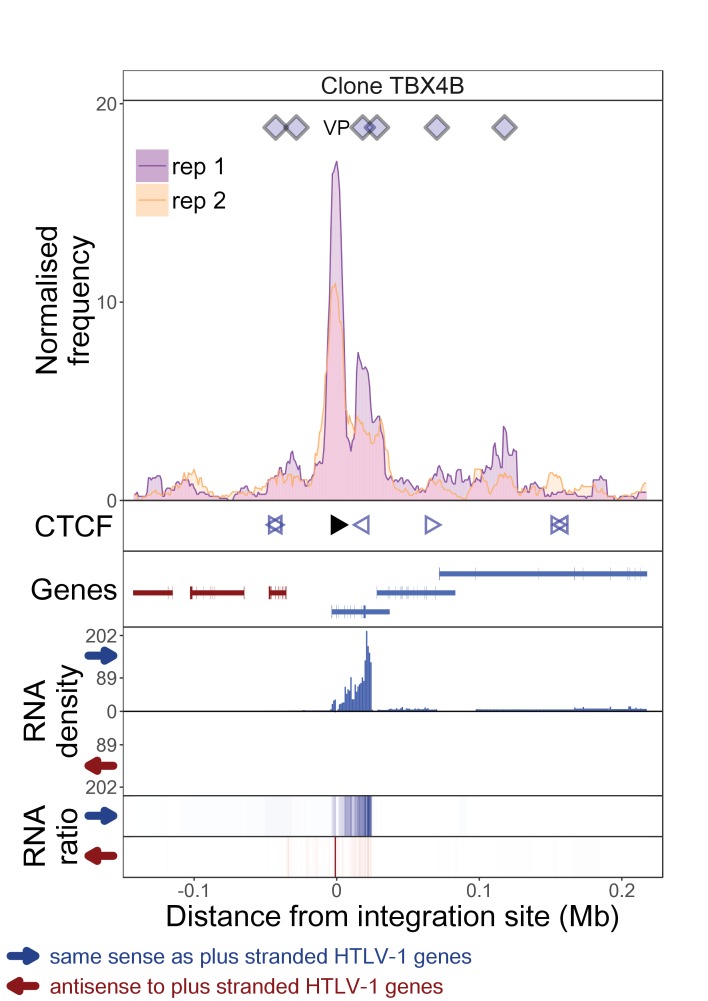
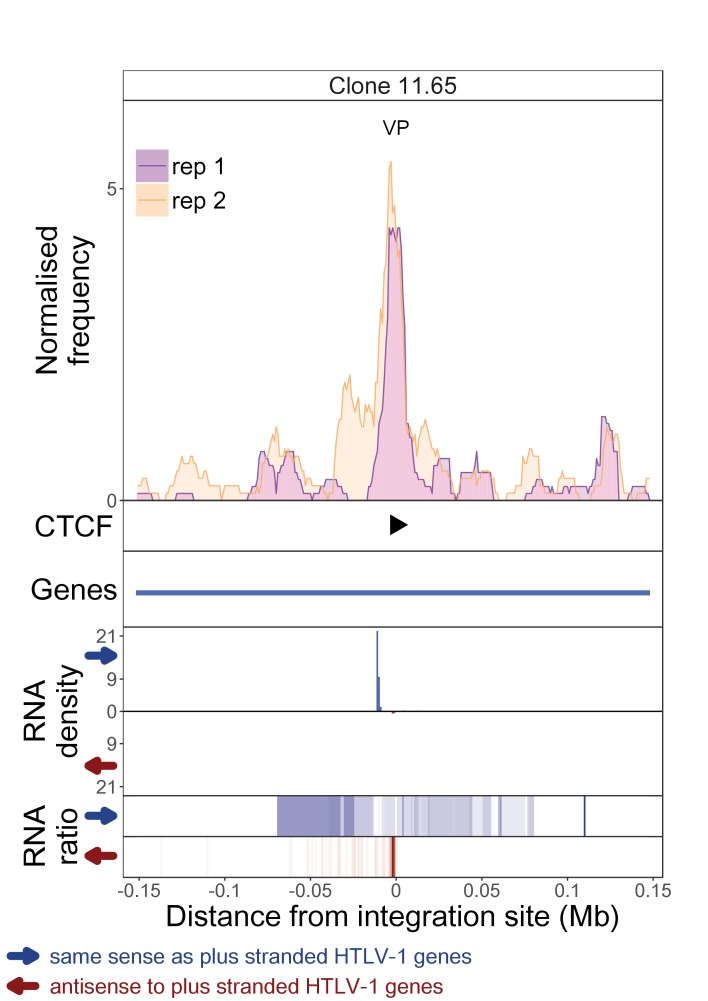
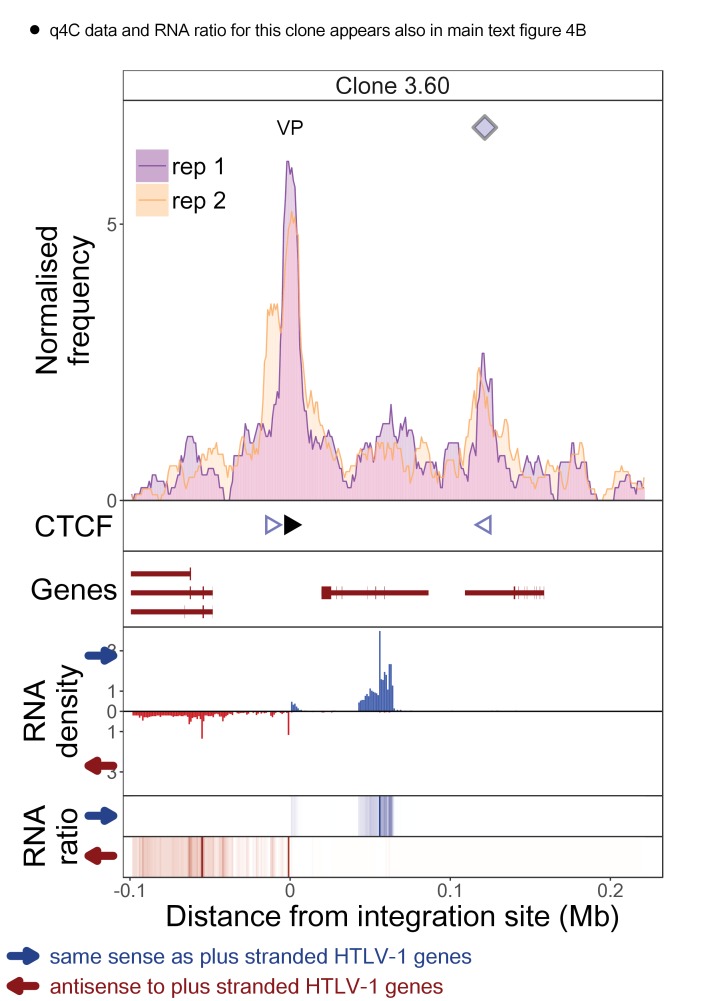
Figure 1. HTLV-1 forms distant contacts with the host genome.
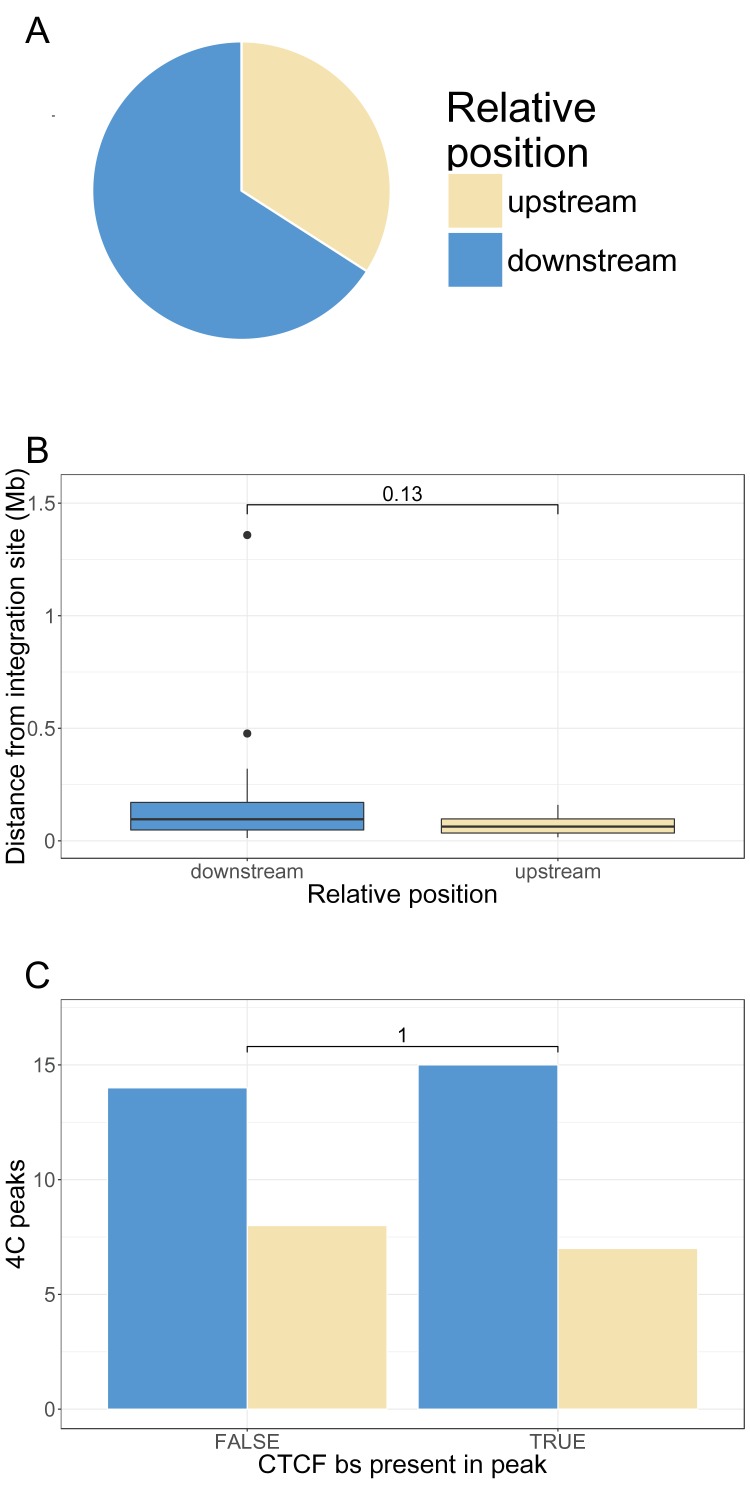
(A) Upper line: the HTLV-1 genome (green), with a long terminal repeat (LTR) at each end, is integrated into a clone-specific site in the human genome (grey). The q4C viewpoint (blue rectangle) is the NlaIII fragment within the HTLV-1 genome (nucleotide residues 6564–7246) which contains the CTCF binding site (CTCF-BS; black arrowhead). Lower line: the CTCF-BS (blue hexagon) in the provirus can dimerize with a CTCF-BS in the flanking host genome. (B) Chromatin contacts identified by q4C in two different clones. For each clone, the top panel depicts the q4C profile in the 5′ and 3′ host genome flanking the provirus (two biological duplicates), quantified as the normalized frequency of ligation events in overlapping windows (window width 10 kb, step 1 kb). On the horizontal axis, positive values denote positions downstream of the provirus (i.e. lying 3′ of the 3′ LTR); negative values denote upstream position. VP – viewpoint in q4C (proviral integration site). Diamonds mark the positions of reproducible chromatin contact sites called by the peak caller (Materials and methods). CTCF panel – open arrowheads denote positions of CTCF-BS; the filled arrowhead denotes the CTCF-BS in the provirus. Genes panel shows RefSeq protein-coding genes in the flanking host genome. The q4C profiles of remaining clones are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1–10. (C) Number of detected peaks in each clone. (D) Distance from detected q4C peaks to the respective proviral integration site.