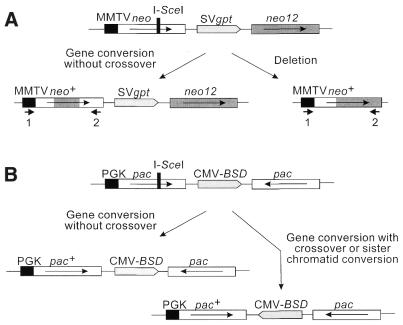
Figure 1.
Structures of recombination substrates and products. (A) 1.4 kb neo direct repeats in CHO strain 33 are shown by open and shaded boxes flanking SVgpt. The upstream neo is driven by the MMTV promoter and an I-SceI recognition site interrupts the reading frame; neo12 has 12 silent RFLP markers (see Fig. 4). Gene conversion without a crossover results in loss of the I-SceI site and transfer of none, one or more markers from neo12, but maintains the gross structure of the substrate. Deletions via SSA, crossovers or unequal sister chromatid exchanges result in loss of one neo and SVgpt. PCR primers 1 and 2 amplify the recipient allele in conversion products and the remaining allele in deletion products. (B) Structure of inverted pac repeats flanking CMV-BSD in human cell line HT1080-1885. The upstream pac is driven by the mouse PGK promoter and inactivated by insertion of an I-SceI site in an 80 bp deletion of the MscI–BssHII fragment in the pac coding sequence. Gene conversion without crossover replaces the I-SceI site and 80 bp deletion with wild-type sequence from the second pac gene. Conversion with crossover or large-scale sister chromatid conversion inverts the central sequences, including CMV-BSD.