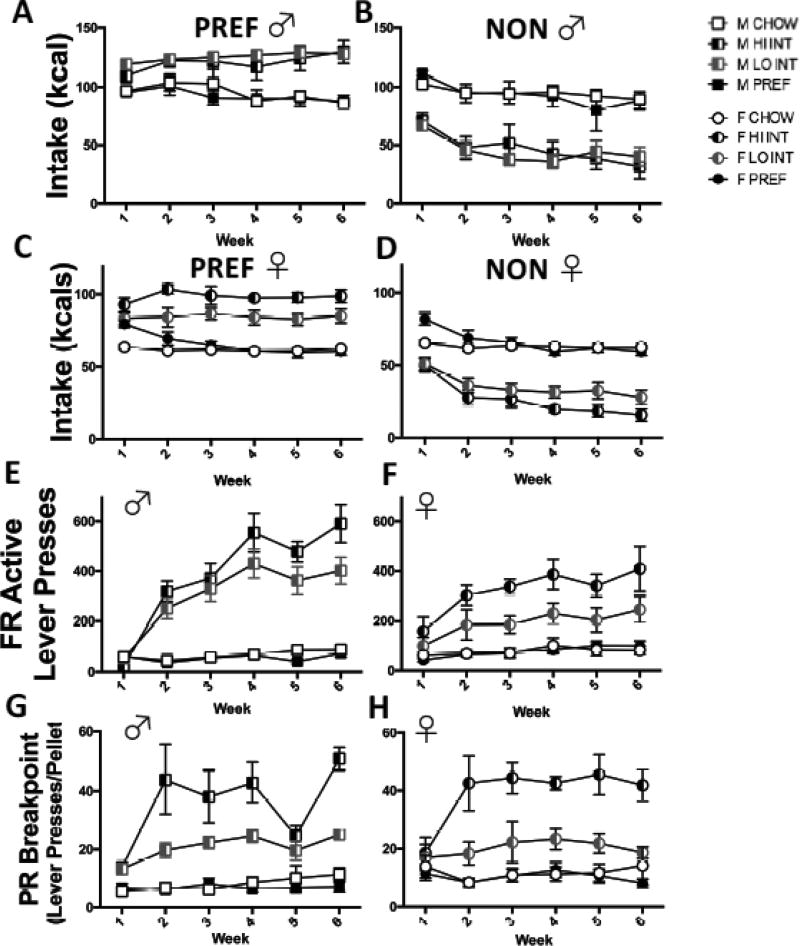
FIG 6.
Consummatory and instrumental behavior differences in high- vs. low-responding INT rats. On PREF days, male HI and LO INTs did not differ from one another (A), but HI INT females overate significantly more on PREF days than their LO INT counterparts (C) (p<0.0001). LO and HI INT rats of both sexes ate more than their CHOW and PREF controls (ps<0.0001). Male HI and LO INTs did not differ from one another (FIG 6B), but HI INT females underate significantly more on NON-PREF days than their LO INT counterparts (FIG 6D) (p<0.02) (see FIGS. 6B and 6D). In both sexes, LO and HI INTs both underate compared to CHOW and PREF rats (ps<0.0001). HI INT rats showed progressively greater active lever presses than LO INT rats, a difference that reached significance by week 4 in males (ps<0.05) (E) and by week 3 in females (ps<0.05) (F). In both sexes, HI INT rats escalated their breakpoints over time (especially from Week 1 to Week 2), whereas LO INT rats did not (G & H) Data show M+SEM. n = 4–10/group.