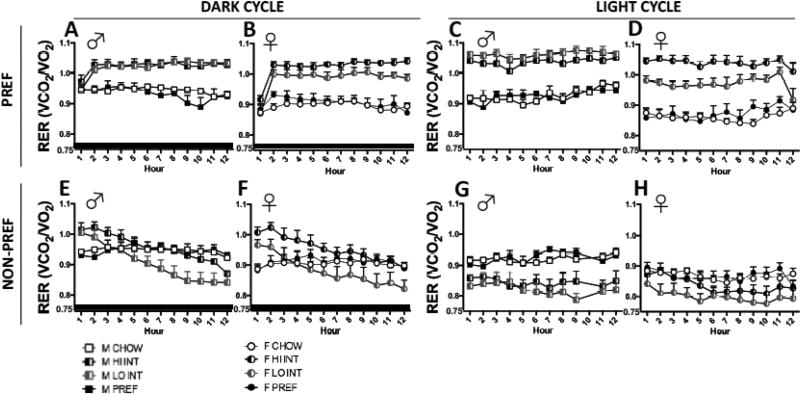
FIG 8.
HI vs LO INT compulsive-like classifications and respiratory exchange ratio (RER). During the PREF phase, HI INT rats had higher RERs than LO INT rats (p<0.0001). This difference was more apparent in females (B & D) than males (A &C) with a greater difference seen during the light cycle (p<0.07). There was a difference seen between HI vs. LO INT females (p<0.02), but not males (p>0.3). HI INT and LOW INT rats of both sexes had greater RERs than CHOW and PREF rats during the dark cycle and throughout the entire light cycle (p<0.0001).
During the NON-PREF phase, in both sexes, HI INT rats showed trends for greater RERs than LO INT rats across the entire dark cycle (E &F). RERs of both HI INT and LO INT rats, but not ad lib controls, decreased steadily across the dark cycle ( p<0.0001). HI INT rats had higher RERs than CHOWs and PREFs during the early of the dark cycle, and LO INT rats had lower RERs than ad lib controls in the late dark cycle, whereas RERs of HI INT rats did not drop significantly below those of controls. During the light cycle of the NON-PREF food phase (G & H), LO INT rats had lower RERs than ad lib controls from the beginning of the light cycle, but RERs of HI INT rats were not reduced immediately.
Data show M+SEM. n = 4–10/group.