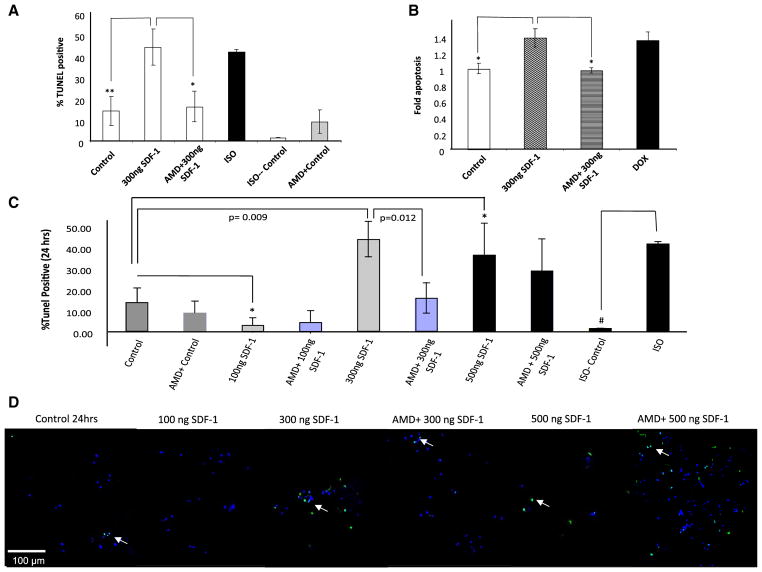
Fig. 1.
SDF-1 concentration dependent effects on cardiomyocytes survival. a, b SDF-1 induces apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Freshly isolated rat cardiomyocytes were treated for 24 h with either 300 ng/ml SDF-1, 1 μM DOX, 100 μM ISO or diluent (ISO control). Pre-treatment with 10 mM AMD for 1 h was followed by a 24 h treatment with 300 ng/ml SDF-1 plus 10 mM AMD. a Apoptosis was detected by using TUNEL and b confirmed with the Cell Death Detection ELISAPLUS by quantization the cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments (n = 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. 300 ng/ml SDF-1). c, d To assess the SDF-1 dose response curve, freshly isolated adult rat cardiomyocyte were treated for 24 h with either SDF-1 (100, 300 or 500 ng/ml) with or without pretreatment with 10 mM AMD3100, specific CXCR4 antagonist for 1 h prior to the treatment. ISO (100 μM) was used as a positive control to induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Apoptosis was detected by using TUNEL assay. A double-staining technique was used i.e., TUNEL staining by using an In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit (Fluorescein) for apoptotic cell nuclei and DAPI (Blue) staining for all cell nuclei. TUNEL positive cells were visualized as indicated by green fluorescence staining and percentage (%) of TUNEL positive cells was determined (i.e., number of TUNEL-positive myocytes/total number of myocytes × 100). Assays were performed in a blinded manner. Three independent experiments were performed, in each experiment, each condition was performed in triplicate (i.e., coverslips from three separate dishes were counted per treatment condition, a total of 15 fields) (n = 15; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, #p < 0.001). d Selective images demonstrating TUNEL positive cells (green signal) for each group are shown