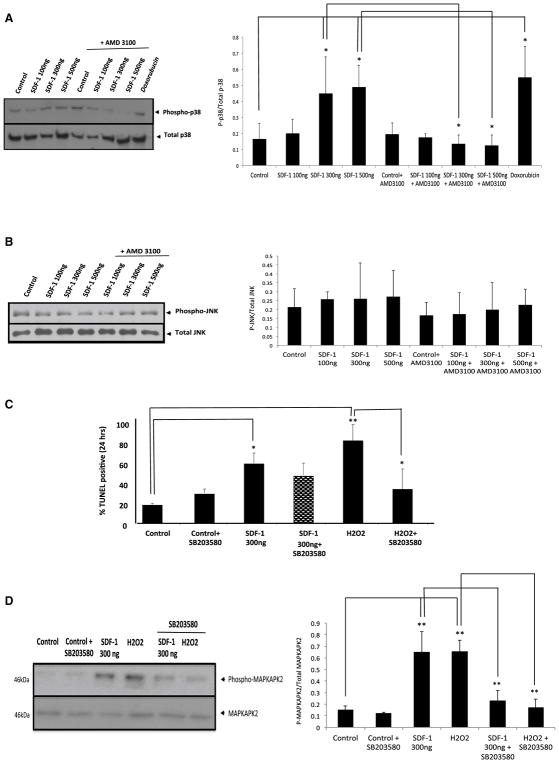
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of the P38 MAPK pathway did not reverses the apoptotic effect of SDF-1. a, b Freshly isolated adult rat cardiomyocyte were treated for 24 h with either 100 or 200 or 500 ng/ml SDF-1, with or without pretreatment with 10 mM AMD3100 (a specific CXCR4 blocking compound) for 1 h, or 1 μM DOX (positive control). Western blot analysis was performed for detection of Phospho-P38 and Phospho-JNK/SAPK primary antibodies. Representative gels; left (phospho-p38) and right (Phospho-JNk/SAPK) panels are shown here. Densitometric analysis of data from three different experiments is shown (lower panels). c To determine the contribution of P38 MAPK on SDF-1-mediated apoptosis, inhibitor of the p38 MAPK (SB203580; 10 μM) were included in the treatment of cultures of adult rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes were pretreated with 10 μM SB203580, p38 inhibitor, for 1 h followed by a 24 h treatment with SDF-1 (300 ng/ml) or H2O2 (positive control to induce apoptosis). Apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay as described before. Percentage (%) of TUNEL positive cells was determined (i.e., number of TUNEL-positive myocytes/total number of myocytes × 100). Assays were performed in a blinded manner. Three independent experiments were performed, in each experiment, each condition was performed in triplicate (i.e., coverslips from three separate dishes were counted per treatment condition, a total of 15 fields) (n = 15; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). d Freshly isolated cardiomyocytes were treated as described before and we used immunoblotting assay for detection of Phospho-MAPKAPK2 and MAPKAPK antibodies (left panel). Densitometric analysis of data from three different experiments is shown (right panel) (n = 3; **p < 0.01 vs. control)