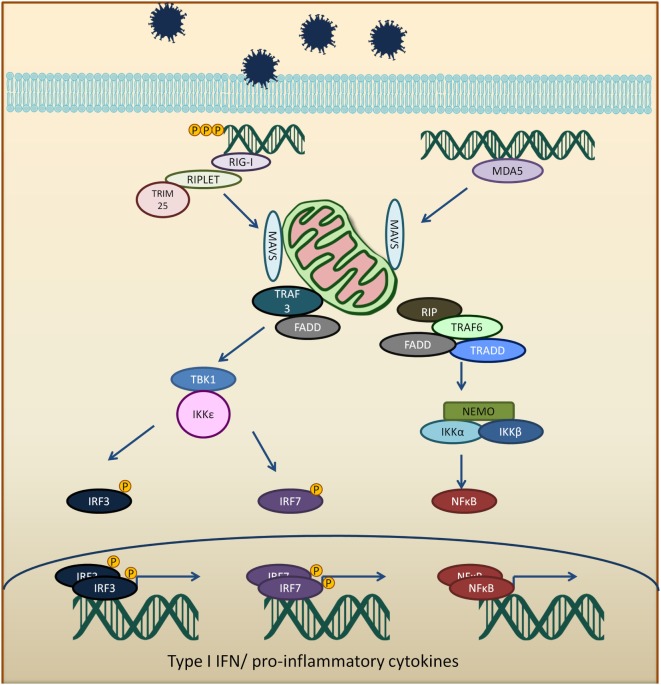
Figure 1.
Viral RNA is recognized by RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), RIG-I, or melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5). Activated RLRs interacts with mitochondria antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) adapter protein via CARD–CARD interactions. Activated MAVS then interacts with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors 3 (TRAF3), tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors 6 (TRAF6), tumor necrosis factor receptor type-1-associated death domain (TRADD), receptor interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIP1), Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD), and other signaling molecules. TRAF3 activates TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and IκB kinase ε (IKKε), which phosphorylates interferon regulatory factors 3 and 7 (IRF3 and IRF7). The phosphorylated IRF3 and IRF7 dimerize and translocate into the nucleus to induce type 1 interferon response. On the other hand, MAVS interaction with receptor interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1, FADD, TRAF6, and TRADD. TRAF 6 ubiquitinate NF-kappa-B essential modulator (NEMO) which then activates IκB kinase and activates NF-κB. NF-κB transcription factor drives the expression of type 1 interferon and proinflammatory cytokines.