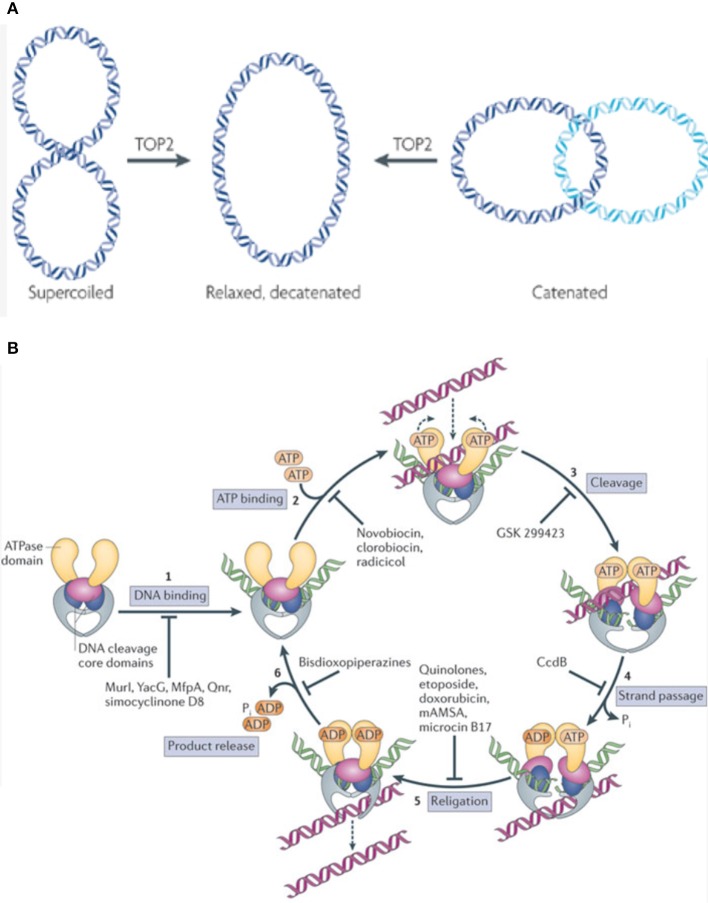
Figure 1.
(A) TOP2 functions by relieving supercoils generated as a function of the double stranded nature of DNA. Additionally, TOP2 removes catenanes (interlinked DNA products) formed during replication. This allows the cell to carry out vital functions like replication, repair, and transcription. Figure modified and reproduced with permission from Nature Publishing Group. (B) TOP2 inhibitors function by interfering with various steps in the enzyme's catalytic cycle. Some Topoisomerase inhibitors work by inhibiting DNA binding, thus preventing the formation of the DNA-enzyme complex (1), while others act at the next step, preventing ATP from binding to the DNA-enzyme complex which in turn does not allow for the formation of a closed clamp structure (2). Some agents prevent the enzymatic generation of a double stranded DNA break (DSB) (3). Other downstream agents function by preventing the passage of the intact strand through the already generated ds-DNA break (4). Etoposide, doxorubicin, and analogous agents function by inhibiting DNA religation, thus stabilizing the DSB-enzyme complex and triggering apoptosis (5). Some inhibitors work at the last step of the catalytic cycle, and preventing the release of product from the enzyme (6). Figure reproduced with permission from Nature Publishing Group.