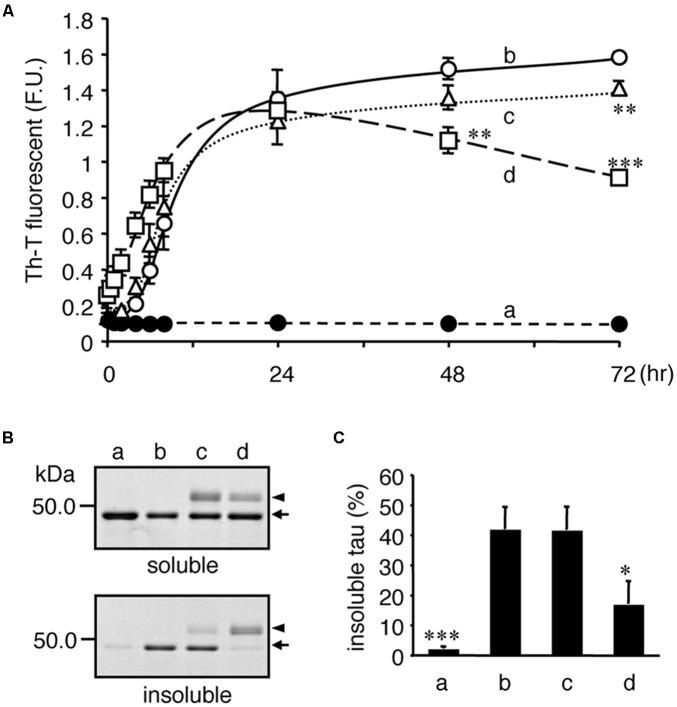
FIGURE 9.
Tubulin inhibits heparin-induced aggregation of tau. Recombinant tau (a–d) and tubulin (0.2 mg/ml; c, 1.0 mg/ml; d) were incubated without (closed: a) or with (open: b–d) heparin at indicated periods. (A) Time courses of Th-T fluorescence change are shown (means ± SEM, n = 4). The statistical significance compared to controls (+heparin, 0 mg/mL tubulin) was analyzed by Tukey’s post hoc test (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001). (B) After 72 hincubation, the proteins were subjected to the Sarkosyl-solubility assay as described in the Materials and Methods section. Gel images of CBB staining of total, Sarkosyl-soluble, and Sarkosyl-insoluble fractions are shown. Arrows and arrowheads indicate tau and tubulin, respectively. Note that the Sarkosyl-insoluble tau was reduced in the presence of tubulin (the arrow in lowest panel). (C) The amounts of Sarkosyl-insoluble tau were quantified (means ± SEM, n = 4). Statistical significance was analyzed by Tukey’s post hoc test (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).