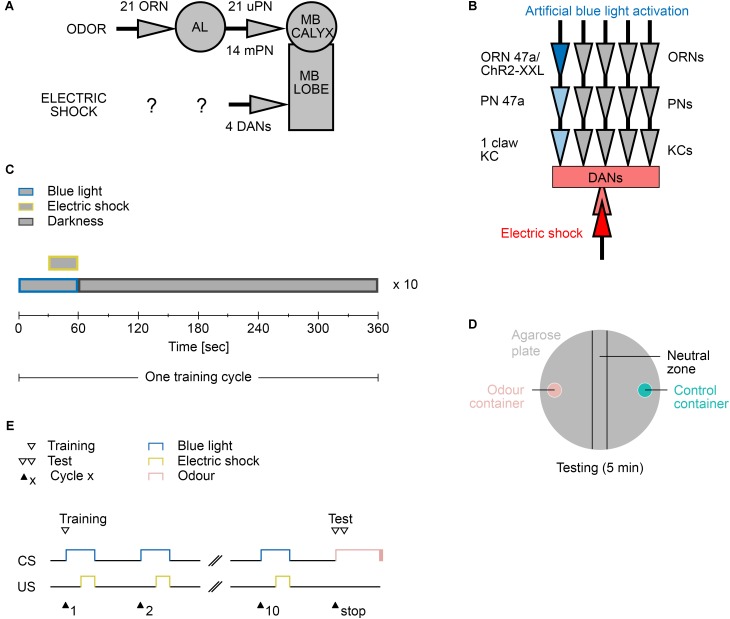
FIGURE 2.
Aversive learning paradigm. (A) The neuronal circuit involved is depicted as the olfactory pathway (CS, on top) and the electric shock pathway (US, bottom). Olfactory information is perceived by only 21 olfactory receptor neurons (ORN) and further processed at the antennal lobe (AL). Second order projections neurons (PN) signal onto third order Kenyon Cell of the mushroom body (MB). There are 21 uni-glomerular PNs and 14 multi-glomerular PNs. Electric shocks are perceived and processed by yet unknown neurons. Further downstream likely four dopaminergic neurons (DAN) signal onto the MB lobes, where CS and US converge. (B) The applied protocol uses blue light activation of the single ORN 47a via Channelrhodopsin2-XXL (ChR2-XXL). Further downstream at the MB this information converges with the applied electric shock dependent activation of DANs. (C) Composition of one training cycle. One cycle comprises a 60 s blue light phase, in which last 30 s an electric shock is applied, and a 300 s darkness phase. The training cycle is repeated ten times. (D) Schematic description of the testing agarose plate. During the testing phase larvae were placed in the beginning in the neutral zone and were left on the plate for 5 min to make a decision between the presented odor (odor container; pink) and control container (empty or containing paraffin oil; turquoise). After testing, all larvae on the odor container side, the control container side, and in the neutral zone were counted. (E) Timescale of the larvae training and testing procedure. CS, conditioned stimulus (blue light); US, unconditioned stimulus (electric shock).