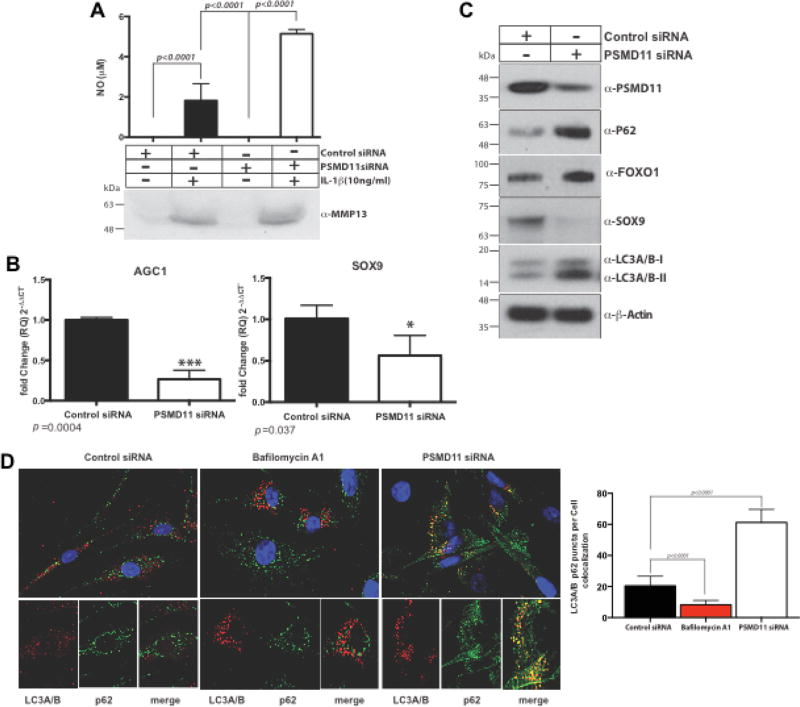
Figure 5. PSMD11 siRNA knockdown induces increased NO release, induces decreases in SOX9 and AGC1, and stimulates elements of the autophagy process, in normal chondrocytes.
We studied PSMD11 siRNA knockdown effects on NO and MMP13 release in response to IL-1β (10 ng/ml) in normal human knee chondrocytes (A). We also analyzed PSMD11 siRNA effects on SOX9 and AGC1 (B), and SOX9 protein expression, as well as autophagy-related LC3A/B-I to LC3A/B-II conversion, the autophagy-UPS adaptor and LC3-binding protein p62 (C), and perinuclear co-localization of p62 and LC3A/B-I to LC3A/B-II in normal chondrocytes (D), with 300 cells/treatment counted to quantify structures where LC3A/B and p62 co-localized. Analysis was by 2-way ANOVA (Multiple comparison with Bonferroni post hoc comparison).